Taohuajing reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy through the sirtuin 1/nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 pathway
- PMID: 33637069
- PMCID: PMC7913206
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-021-03218-0
Taohuajing reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy through the sirtuin 1/nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 pathway
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress and inflammation promote the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM). Therefore, inhibiting these processes may show beneficial effects in the treatment of patients with DCM. Taohuajing (THJ) is prepared using Persicae semen (Taoren), Polygonatum sibiricum (Huangjing), and Carthami flos (Honghua) and may have applications in the treatment of DCM. However, the protective effects of THJ have not been thoroughly assessed. Accordingly, in this study, we aimed to investigate the protective effects of THJ in a model of DCM and further clarify the potential mechanisms.
Methods: A type 2 diabetes mellitus model was generated using male C57BL/6 mice. Echocardiography and histopathology were used to evaluate cardiac function. The expression levels of cytokines were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Western blotting and small interfering RNA were used to evaluate the targets of THJ.
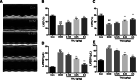
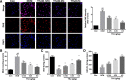
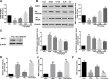
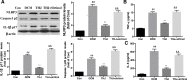
Results: Compared with the control group, DCM mice showed cardiac dysfunction, metabolic disorder, fibrosis, and disorganized ultrastructure, and THJ treatment significantly inhibited these changes significantly. THJ treatment also inhibited the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA), induced the production of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), decreased the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and suppressed the activation of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. These protective effects were abolished by sirtinol, an inhibitor of sirtuin1 (SIRT1).
Conclusions: Overall, THJ protected the heart from hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in DCM mice via a mechanism involving SIRT1-mediated antioxidant proteins and suppression of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Keywords: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; Inflammation; NLRP3; Oxidative stress; Sirtuin 1; Taohuajing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2015SF2-08-01/Key Research and Development Plan Projects of Shaanxi Province in China
- No. 2015-164/the Key Research Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Natural Medicine in Shaanxi Province
- No.S2018-ZC-GCZXXY-SF-0005/the subsidy after Project of Shaanxi Engineering Technology Research Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

