RBM15 facilitates laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3 dependent
- PMID: 33637103
- PMCID: PMC7912894
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01871-4
RBM15 facilitates laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3 dependent
Abstract
Background: Laryngeal cancer has the highest mortality rate among head and neck tumours. RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most plentiful and variable in mammalian mRNA. Yet, the m6A regulatory mechanism underlying the carcinogenesis or progression of LSCC remains poorly understood.
Methods: The m6A RNA methylation quantification kit was used to detect tissue methylation levels. m6A microarray analysis, mRNA transcriptomic sequencing (mRNA-seq), and proteomics were used to determine RBM15, TMBIM6, and IGF2BP3. Immunohistochemical (IHC), quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot were used to investigate RBM15, TMBIM6, and IGF2BP3 expression in tissue samples and cell lines. The biological effects of RBM15 were detected both in vitro and in vivo. The combination relationship between RBM15/IGF2BP3 and TMBIM6 was verified by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay, Methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq), RNase Mazf, and luciferase report assay. RNase Mazf was used to determine the methylation site on TMBIM6 mRNA. Hoechst staining assay was used to confirm the apoptotic changes. The actinomycin D verified TMBIM6 stability.
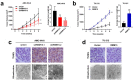
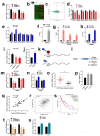
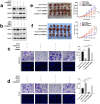
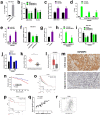
Results: The global mRNA m6A methylation level significantly increased in LSCC patients. RBM15, as a "writer" of methyltransferase, was significantly increased in LSCC and was associated with unfavorable prognosis. The knockdown of RBM15 reduced the proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis of LSCC both in vitro and in vivo. The results were reversed after overexpressing RBM15. Mechanically, TMBIM6 acted as a downstream target of RBM15-mediated m6A modification. Furthermore, RBM15-mediated m6A modification of TMBIM6 mRNA enhanced TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3-dependent.
Conclusion: Our results revealed the essential roles of RBM15 and IGF2BP3 in m6A methylation modification in LSCC, thus identifying a novel RNA regulatory mechanism.
Keywords: IGF2BP3; Laryngeal squamous cell cancer (LSCC); N6-methyladenosine (m6A); RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15); TMBIM6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RBM15 recruits myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the m6A-IGF2BP3/CBR3-AS1/miR-409-3p/CXCL1 axis, facilitating radioresistance in non-small-cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 17;23(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06205-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39962467 Free PMC article.
-
IGF2BP3 Regulates TMA7-mediated Autophagy and Cisplatin Resistance in Laryngeal Cancer via m6A RNA Methylation.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Feb 22;19(5):1382-1400. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.80921. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37056932 Free PMC article.
-
STRIP2 motivates non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating the TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3 dependent.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jan 13;42(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02573-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36639675 Free PMC article.
-
RBM15 facilities lung adenocarcinoma cell progression by regulating RASSF8 stability through N6 Methyladenosine modification.Transl Oncol. 2024 Aug;46:102018. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102018. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38838436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): current status and future insights.Med Oncol. 2024 Nov 24;42(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02566-4. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39580759 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibiting the m6A Reader IGF2BP3 Suppresses Ovarian Cancer Cell Growth via Regulating PLAGL2 mRNA Stabilization.World J Oncol. 2024 Feb;15(1):100-113. doi: 10.14740/wjon1747. Epub 2024 Jan 10. World J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38274714 Free PMC article.
-
Cucurbitacin E elicits apoptosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by enhancing reactive oxygen species-regulated mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 25;14(8):3905-3921. doi: 10.62347/HPQQ9412. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39267666 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes From Cancer-Associated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transmit TMBIM6 to Promote the Malignant Behavior of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Activating PI3K/AKT Pathway.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 2;12:868726. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.868726. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. Retraction in: Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 19;13:1307333. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1307333. PMID: 35720012 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The Interaction Between N6-Methyladenosine Modification and Non-Coding RNAs in Gastrointestinal Tract Cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 7;11:784127. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.784127. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35070987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase FTO Promotes Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Proliferation and Migration by Increasing CTNNB1.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Nov 24;14:8785-8795. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S339095. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34853532 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

