SMYD3: a regulator of epigenetic and signaling pathways in cancer
- PMID: 33637115
- PMCID: PMC7912509
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-021-01021-9
SMYD3: a regulator of epigenetic and signaling pathways in cancer
Abstract
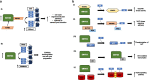
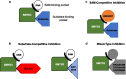
Chromatin modifiers and their implications in oncogenesis have been an exciting area of cancer research. These are enzymes that modify chromatin via post-translational modifications such as methylation, acetylation, sumoylation, phosphorylation, in addition to others. Depending on the modification, chromatin modifiers can either promote or repress transcription. SET and MYN-domain containing 3 (SMYD3) is a chromatin modifier that has been implicated in the development and progression of various cancer types. It was first reported to tri-methylate Histone 3 Lysine 4 (H3K4), a methylation mark known to promote transcription. However, since this discovery, other histone (H4K5 and H4K20, for example) and non-histone (VEGFR, HER2, MAP3K2, ER, and others) substrates of SMYD3 have been described, primarily in the context of cancer. This review aims to provide a background on basic characteristics of SMYD3, such as its protein structure and tissue expression profiles, discuss reported histone and non-histone substrates of SMYD3, and underscore prognostic and functional implications of SMYD3 in cancer. Finally, we briefly discuss ongoing efforts to develop inhibitors of SMYD3 for future therapeutic use. It is our hope that this review will help synthesize existing research on SMYD3 in an effort to propel future discovery.
Keywords: Chromatin modifier; Histone methylation; Non-histone methylation; SMYD3; SMYD3 cancer implications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

