Non-uremic calciphylaxis in a woman without end-stage renal disease
- PMID: 33637497
- PMCID: PMC7919574
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-239225
Non-uremic calciphylaxis in a woman without end-stage renal disease
Abstract
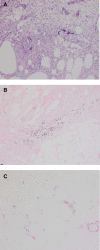
A woman in her 60s with a history of lower extremity vascular disease presented with extreme pain and wounds in her legs which had kept her from walking for several weeks. The patient's pain became intolerable throughout her hospital stay despite multiple surgical revascularisations. Biopsy of the patient's calf wounds revealed evidence of calciphylaxis, a diagnosis which corresponds with this patient's extreme pain. Our patient had no history of end-stage renal disease.
Keywords: dermatology; renal medicine.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Breast lesions with intractable pain in end-stage renal disease: calciphylaxis with chronic hypotensive dermatopathy related watershed breast lesions.J Palliat Med. 2013 May;16(5):551-4. doi: 10.1089/jpm.2012.0495. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Palliat Med. 2013. PMID: 23531028
-
Calciphylaxis in the absence of pathological skin lesions.BMJ Case Rep. 2025 Feb 11;18(2):e264176. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2024-264176. BMJ Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39933861
-
Calciphylaxis: Case Presentation and Review of the Literature.J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2018 Nov/Dec;45(6):532-535. doi: 10.1097/WON.0000000000000473. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2018. PMID: 30216332
-
Management of Cutaneous Calciphylaxis.Adv Ther. 2020 Dec;37(12):4797-4807. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01504-w. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32997277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calciphylaxis: case report and literature review.Afr J Med Med Sci. 2002 Jun;31(2):175-8. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2002. PMID: 12518918 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
