Recovery of early postoperative muscle strength after deep neuromuscular block by means of ultrasonography with comparison of neostigmine versus sugammadex as reversal drugs: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 33637547
- PMCID: PMC7919596
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043935
Recovery of early postoperative muscle strength after deep neuromuscular block by means of ultrasonography with comparison of neostigmine versus sugammadex as reversal drugs: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the use of quantitative neuromuscular monitoring together with the administration of reversal drugs (neostigmine or sugammadex), the incidence of residual neuromuscular blockade defined as a train-of-four ratio (TOFr) <0.9 remains high. Even TOFr >0.9 cannot ensure adequate recovery of neuromuscular function when T1 height is not recovered completely. Thus, a mathematical correction of TOFr needs to be applied because the return of a normal TOFr can precede the return of a normal T1 twitch height. On the other hand, different muscles have different sensitivities to neuromuscular blockade agents; thus, complete recovery of one specific muscle group does not represent complete recovery of all other muscles. Therefore, our study aims to assess the muscle strength recovery of respiratory-related muscle groups by ultrasound and evaluate global strength using handgrip dynamometry in the early postoperative period when TOFr=0.9 and corrected TOFr (cTOFr)=0.9 with comparison of neostigmine versus sugammadex as reversal drugs.
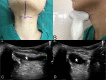
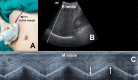
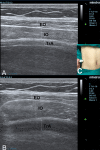
Methods and analysis: This study will be a prospective, single-blinded, randomised controlled trial involving 60 patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I-II and aged between 18 and 65 years, who will undergo microlaryngeal surgery. We will assess geniohyoid muscle, parasternal intercostal muscle, diaphragm, abdominal wall muscle and handgrip strength at four time points: before anaesthesia, TOFr=0.9, cTOFr=0.9 and 30 min after admission to the post anaesthesia care unit. Our primary objective will be to compare the effects of neostigmine and sugammadex on the recovery of muscle strength of different muscle groups in the early postoperative period when TOFr=0.9 and cTOFr=0.9. The secondary objective will be to observe the difference of muscle strength between the time points of TOFr=0.9 and cTOFr=0.9 to find out the clinical significance of cTOFr >0.9.
Ethics and dissemination: The protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University. The findings will be disseminated to the public through peer-reviewed scientific journals.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR2000033832.
Keywords: adult anaesthesia; clinical trials; ultrasonography.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recovery of muscle function after deep neuromuscular block by means of diaphragm ultrasonography and adductor of pollicis acceleromyography with comparison of neostigmine vs. sugammadex as reversal drugs: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Feb 21;19(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2525-7. Trials. 2018. PMID: 29467022 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal with sugammadex in the absence of monitoring did not preclude residual neuromuscular block.Anesth Analg. 2013 Aug;117(2):345-51. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182999672. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Anesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 23757472
-
Sugammadex Versus Neostigmine for Recovery of Respiratory Muscle Strength Measured by Ultrasonography in the Postextubation Period: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Anesth Analg. 2023 Mar 1;136(3):559-568. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000006219. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Anesth Analg. 2023. PMID: 36279410 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Failure of reversion of neuromuscular block with sugammadex in patient with myasthenia gravis: case report and brief review of literature.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Aug 17;19(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0829-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 31421671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of sugammadex compared to neostigmine for reversal of neuromuscular blockade: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Clin Anesth. 2016 Dec;35:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.06.018. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Clin Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27871504 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative efficacy of sugammadex and neostigmine in postoperative nausea and vomiting management: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Anesth. 2025 Aug;39(4):637-651. doi: 10.1007/s00540-025-03498-7. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Anesth. 2025. PMID: 40293461 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
