Identification and Predictions Regarding the Biosynthesis Pathway of Polyene Macrolides Produced by Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63
- PMID: 33637575
- PMCID: PMC8117769
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03157-20
Identification and Predictions Regarding the Biosynthesis Pathway of Polyene Macrolides Produced by Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63
Erratum in
-
Correction for Han et al., "Identification and Predictions Regarding the Biosynthesis Pathway of Polyene Macrolides Produced by Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63".Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Jun 11;87(13):e0080221. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00802-21. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34114900 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
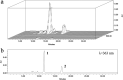
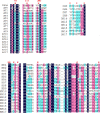
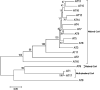
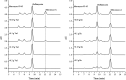
A group of polyene macrolides mainly composed of two constituents was isolated from the fermentation broth of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63, which was isolated from soil where potato scabs were repressed naturally. One of these macrolides was roflamycoin, which was first reported in 1968, and the other was a novel compound named Men-myco-A, which had one methylene unit more than roflamycoin. Together, they were designated RM. This group of antibiotics exhibited broad-spectrum antifungal activities in vitro against 17 plant-pathogenic fungi, with 50% effective concentrations (EC50) of 2.05 to 7.09 μg/ml and 90% effective concentrations (EC90) of 4.32 to 54.45 μg/ml, which indicates their potential use in plant disease control. Furthermore, their biosynthetic gene cluster was identified, and the associated biosynthetic assembly line was proposed based on a module and domain analysis of polyketide synthases (PKSs), supported by findings from gene inactivation experiments.IMPORTANCEStreptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 is a biocontrol strain that has been studied in our laboratory for many years and exhibits a good inhibitory effect in many crop diseases. Therefore, the identification of antimicrobial metabolites is necessary and our main objective. In this work, chemical, bioinformatic, and molecular biological methods were combined to identify the structures and biosynthesis of the active metabolites. This work provides a new alternative agent for the biological control of plant diseases and is helpful for improving both the properties and yield of the antibiotics via genetic engineering.
Keywords: Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63; antibiotic; antifungal activity; biosynthetic gene cluster; polyene macrolide.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


References
-
- Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O'Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA. 2002. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147. 10.1038/417141a. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Letek M, Mateos LM, Gil JA. 2014. Genetic analysis and manipulation of polyene antibiotic gene clusters as a way to produce more effective antifungal compounds, p 177–214. In Antimicrobial compounds. Springer, New York, NY.
-
- Brautaset T, Sekurova ON, Sletta H, Ellingsen TE, StrŁm AR, Valla S, Zotchev SB. 2000. Biosynthesis of the polyene antifungal antibiotic nystatin in Streptomyces noursei ATCC 11455: analysis of the gene cluster and deduction of the biosynthetic pathway. Chem Biol 7:395–403. 10.1016/S1074-5521(00)00120-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

