Identification of Fungal Limonene-3-Hydroxylase for Biotechnological Menthol Production
- PMID: 33637576
- PMCID: PMC8117750
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02873-20
Identification of Fungal Limonene-3-Hydroxylase for Biotechnological Menthol Production
Abstract
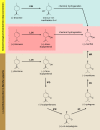
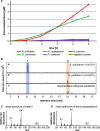
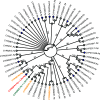
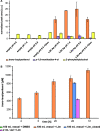
More than 30,000 tons of menthol are produced every year as a flavor and fragrance compound or as a medical component. So far, only extraction from plant material and chemical synthesis are possible. An alternative approach for menthol production could be a biotechnological-chemical process with ideally only two conversion steps, starting from (+)-limonene, which is a side product of the citrus processing industry. The first step requires a limonene-3-hydroxylase (L3H) activity that specifically catalyzes hydroxylation of limonene at carbon atom 3. Several protein engineering strategies have already attempted to create limonene-3-hydroxylases from bacterial cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (CYPs, or P450s), which can be efficiently expressed in bacterial hosts. However, their regiospecificity is rather low compared to that of the highly selective L3H enzymes from the biosynthetic pathway for menthol in Mentha species. The only naturally occurring limonene-3-hydroxylase activity identified in microorganisms so far was reported for a strain of the black yeast-like fungus Hormonema sp. in South Africa. We have discovered additional fungi that can catalyze the intended reaction and identified potential CYP-encoding genes within the genome sequence of one of the strains. Using heterologous gene expression and biotransformation experiments in yeasts, we were able to identify limonene-3-hydroxylases from Aureobasidium pullulans and Hormonema carpetanum Further characterization of the A. pullulans enzyme demonstrated its high stereospecificity and regioselectivity, its potential for limonene-based menthol production, and its additional ability to convert α- and β-pinene to verbenol and pinocarveol, respectively.IMPORTANCE (-)-Menthol is an important flavor and fragrance compound and furthermore has medicinal uses. To realize a two-step synthesis starting from renewable (+)-limonene, a regioselective limonene-3-hydroxylase enzyme is necessary. We identified enzymes from two different fungi which catalyze this hydroxylation reaction and represent an important module for the development of a biotechnological process for (-)-menthol production from renewable (+)-limonene.
Keywords: CYP; P450; biotechnology; fungal enzyme; fungal enzymes; hydroxylation; limonene; menthol; oxidation; terpenes.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regiospecific cytochrome P450 limonene hydroxylases from mint (Mentha) species: cDNA isolation, characterization, and functional expression of (-)-4S-limonene-3-hydroxylase and (-)-4S-limonene-6-hydroxylase.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999 Aug 1;368(1):181-92. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1298. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999. PMID: 10415126
-
Hydroxylation of limonene enantiomers and analogs by recombinant (-)-limonene 3- and 6-hydroxylases from mint (Mentha) species: evidence for catalysis within sterically constrained active sites.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001 Mar 1;387(1):125-36. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.2248. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11368174
-
A Fungal P450 Enzyme from Thanatephorus cucumeris with Steroid Hydroxylation Capabilities.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jun 18;84(13):e00503-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00503-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29728383 Free PMC article.
-
The current status of Aureobasidium pullulans in biotechnology.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018 Mar;63(2):129-140. doi: 10.1007/s12223-017-0561-4. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018. PMID: 29079936 Review.
-
Cytochrome P450 limonene hydroxylases of Mentha species.Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 1995;12(3-4):245-60. doi: 10.1515/dmdi.1995.12.3-4.245. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 1995. PMID: 8820855 Review.
References
-
- Schäfer B. 2013. Menthol. Chemie Unserer Z 47:174–182. 10.1002/ciuz.201300599. - DOI
-
- van Dyk MS, van Rensburg E, Moleleki N. 1998. Hydroxylation of (+)-limonene, (−)-alpha-pinene and (−)-beta-pinene by a Hormonema sp. Biotechnol Lett 20:431–436. 10.1023/A:1005399918647. - DOI
-
- van Dyk MS, van Rensburg E, Rensburg IPB, Moleleki N. 1998. Biotransformation of monoterpenoid ketones by yeasts and yeast-like fungi. J Mol Catal B Enzym 5:149–154. 10.1016/S1381-1177(98)00024-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

