Semiautomatic Tumor Delineation for Evaluation of 64Cu-DOTATATE PET/CT in Patients with Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Prognostication Based on Lowest Lesion Uptake and Total Tumor Volume
- PMID: 33637589
- PMCID: PMC8612344
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.120.258392
Semiautomatic Tumor Delineation for Evaluation of 64Cu-DOTATATE PET/CT in Patients with Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Prognostication Based on Lowest Lesion Uptake and Total Tumor Volume
Abstract
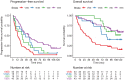
Patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) have heterogeneous somatostatin receptor expression, with highly differentiated lesions having higher expression. Receptor expression of the total tumor burden may be visualized by somatostatin receptor imaging, such as with 64Cu-DOTATATE PET/CT. Assessment of maximal lesion uptake is associated with progression-free survival (PFS) but not overall survival (OS). We hypothesized that the lesion with the lowest, rather than the highest, 64Cu-DOTATATE uptake would be more prognostic, and we developed a semiautomatic method for evaluating this hypothesis. Methods: Patients with NENs underwent 64Cu-DOTATATE PET/CT. A standardized semiautomatic tumor delineation method was developed and used to identify the lesion with the lowest uptake, that is, with the lowest SUVmean Additionally, we assessed total tumor volume derived from the semiautomatic tumor delineation. Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses were used to determine whether there was any association with OS and PFS. Results: In 116 patients with NENs, median PFS (95% CI) was 23 mo (range, 20-31 mo) and median OS was 85 mo (range, 68-113 mo). Minimum SUVmean and total tumor volume were significantly associated with PFS and OS in univariate Cox regression analyses, whereas SUVmax was significant only for PFS. In multivariate Cox analyses, both minimum SUVmean and total tumor volume remained statistically significant. Minimum SUVmean and total tumor volume were then dichotomized by their median, and patients were categorized into 4 groups: high or low total tumor volume and high or low minimum SUVmean Patients with a low total tumor volume and high minimum SUVmean had a hazard ratio of 0.32 (95% CI, 0.20-0.51) for PFS and 0.24 (95% CI, 0.13-0.43) for OS, both with P values of less than 0.001 (reference: high total tumor volume and low minimum SUVmean). Conclusion: We propose a standardized semiautomatic tumor delineation method to identify the lesion with the lowest 64Cu-DOTATATE uptake and total tumor volume. Assessment of the lowest, rather than the highest, lesion uptake greatly increases prognostication by 64Cu-DOTATATE PET/CT. Combining lesion uptake and total tumor volume, we derived a novel prognostic classification system for patients with NENs.
Keywords: 64Cu-DOTATATE PET; minimum SUVmean; neuroendocrine neoplasms; semiautomatic tumor delineation; total tumor volume.
© 2021 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Digestive System Tumours. 5th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2019:16–19.
-
- Couvelard A, Deschamps L, Ravaud P, et al. . Heterogeneity of tumor prognostic markers: a reproducibility study applied to liver metastases of pancreatic endocrine tumors. Mod Pathol. 2009;22:273–281. - PubMed
-
- Miller HC, Drymousis P, Flora R, Goldin R, Spalding D, Frilling A. Role of Ki-67 proliferation index in the assessment of patients with neuroendocrine neoplasias regarding the stage of disease. World J Surg. 2014;38:1353–1361. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Tang LH, Klimstra DS. Effect of tumor heterogeneity on the assessment of Ki67 labeling index in well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors metastatic to the liver: implications for prognostic stratification. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:853–860. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
