Long non-coding RNA Lnc-LALC facilitates colorectal cancer liver metastasis via epigenetically silencing LZTS1
- PMID: 33637680
- PMCID: PMC7910484
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03461-w
Long non-coding RNA Lnc-LALC facilitates colorectal cancer liver metastasis via epigenetically silencing LZTS1
Abstract
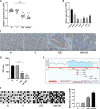
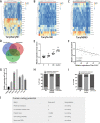
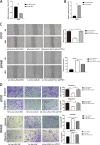
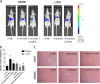
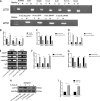
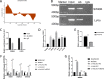
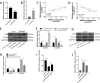
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers around the world and endangers human health seriously. Liver metastasis is an important factor affecting the long-term prognosis of CRC and the specific mechanism of CRLM (colorectal cancer with liver metastasis) is not fully understood. LZTS1 has been found dysregulated in many cancers, especially in CRC. Theories suggested that hypermethylation of the promoter regions of LZTS1 was responsible for LZTS1 abnormal expression in multiple malignant tumors. Although the role of LZTS1 in CRC cell proliferation has been reported, its role in CRLM remains unclear. Numerous studies reported Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) could regulate the gene expression level by regulating gene methylation status in many tumors. However, whether there were lncRNAs could change the methylation status of LZTS1 or not in CRLM was unknown. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether there are lncRNAs can regulate the expression of LZTS1 through affecting DNA methylation in CRLM. We found that upregulated Lnc-LALC in CRC was negatively correlated with LZTS1 expression, and Lnc-LALC could regulate LZTS1 expression in both mRNA and protein level in our study. Functionally, Lnc-LALC enhanced the CRC cells metastasis ability in vitro and vivo through inhibiting the expression of LZTS1. Furthermore, the precise mechanisms exploration showed that lnc-LALC could recruit DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) to the LZTS1 promoter by combining with Enhancer of zeste homolog 2(EZH2) and then altered the expression of LZTS1 via DNMTs-mediated DNA methylation. Collectively, our data demonstrated the important role of Lnc-LALC/ LZTS1 axis in CRLM development.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The tumor-suppressor gene LZTS1 suppresses colorectal cancer proliferation through inhibition of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway.Cancer Lett. 2015 Apr 28;360(1):68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25667121
-
A novel long non-coding RNA lnc-GNAT1-1 is low expressed in colorectal cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor through regulating RKIP-NF-κB-Snail circuit.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 3;35(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0467-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27912775 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA SNHG14 facilitates colorectal cancer metastasis through targeting EZH2-regulated EPHA7.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jul 4;10(7):514. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1707-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31273190 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the ncRNA landscape that governs colorectal cancer: A roadmap to personalized therapeutics.Life Sci. 2024 Oct 1;354:122946. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122946. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39122108 Review.
-
Therapeutic Potentials of MiRNA for Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Treatment: A Narrative Review.Iran J Med Sci. 2025 Apr 1;50(4):202-219. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2024.102910.3622. eCollection 2025 Apr. Iran J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40255223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote osteoblast proliferation, migration and inhibit apoptosis by regulating KLF3-AS1/miR-338-3p.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Feb 9;25(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07236-0. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38336637 Free PMC article.
-
Localization and density of tertiary lymphoid structures associate with molecular subtype and clinical outcome in colorectal cancer liver metastases.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Feb;11(2):e006425. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006425. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36759015 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 15;41(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02319-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35292092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The crosstalk between anoikis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and their synergistic roles in predicting prognosis in colon adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 7;13:1184215. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1184215. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37350934 Free PMC article.
-
GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1.Open Life Sci. 2025 Apr 29;20(1):20251084. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1084. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40321159 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

