SIRT1 attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via Beclin1 deacetylation-mediated autophagy activation
- PMID: 33637691
- PMCID: PMC7910451
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03508-y
SIRT1 attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via Beclin1 deacetylation-mediated autophagy activation
Abstract
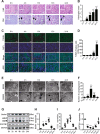
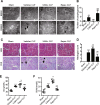
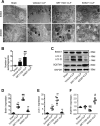
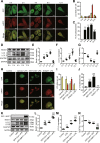
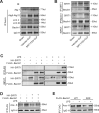
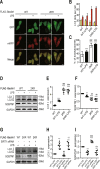
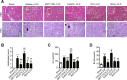
Our previous studies showed that silent mating-type information regulation 2 homologue-1 (SIRT1, a deacetylase) upregulation could attenuate sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (SAKI). Upregulated SIRT1 can deacetylate certain autophagy-related proteins (Beclin1, Atg5, Atg7 and LC3) in vitro. However, it remains unclear whether the beneficial effect of SIRT1 is related to autophagy induction and the underlying mechanism of this effect is also unknown. In the present study, caecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced mice, and an LPS-challenged HK-2 cell line were established to mimic a SAKI animal model and a SAKI cell model, respectively. Our results demonstrated that SIRT1 activation promoted autophagy and attenuated SAKI. SIRT1 deacetylated only Beclin1 but not the other autophagy-related proteins in SAKI. SIRT1-induced autophagy and its protective effect against SAKI were mediated by the deacetylation of Beclin1 at K430 and K437. Moreover, two SIRT1 activators, resveratrol and polydatin, attenuated SAKI in CLP-induced septic mice. Our study was the first to demonstrate the important role of SIRT1-induced Beclin1 deacetylation in autophagy and its protective effect against SAKI. These findings suggest that pharmacologic induction of autophagy via SIRT1-mediated Beclin1 deacetylation may be a promising therapeutic approach for future SAKI treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
p53 Deacetylation Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Promoting Autophagy.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 14;12:685523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.685523. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34335587 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1/3 Activation by Resveratrol Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury in a Septic Rat Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:7296092. doi: 10.1155/2016/7296092. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 28003866 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation suppresses sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Jan 1;316(1):F20-F31. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00119.2018. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30379096
-
[The advances on autophagy the pathogenesis and treatment in septic acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Feb;37(2):183-187. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240904-00748. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40017369 Review. Chinese.
-
Lactate-mitochondrial crosstalk: A new direction in the treatment of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Cell Biol Int. 2024 Nov;48(11):1621-1624. doi: 10.1002/cbin.12240. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Cell Biol Int. 2024. PMID: 39252385 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppresses mitophagy through disturbing the protein interaction of PINK1-Parkin in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jul 2;15(7):473. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06826-z. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38956064 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in acute kidney injury and maladaptive kidney repair.Burns Trauma. 2023 Jan 22;11:tkac059. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkac059. eCollection 2023. Burns Trauma. 2023. PMID: 36694860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocatechualdehyde Rescues Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Endothelial Cells Injury by Inducing Autophagy and Inhibiting Apoptosis via Regulation of SIRT1.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 31;13:846513. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.846513. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35431914 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic dysregulation of autophagy in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: the underlying mechanisms for renoprotection.Front Immunol. 2023 May 5;14:1180866. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1180866. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37215112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of inflammatory response and metabolic reprogramming in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1487576. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1487576. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

