Cell polarisation in a bulk-surface model can be driven by both classic and non-classic Turing instability
- PMID: 33637746
- PMCID: PMC7910310
- DOI: 10.1038/s41540-021-00173-x
Cell polarisation in a bulk-surface model can be driven by both classic and non-classic Turing instability
Abstract
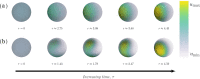
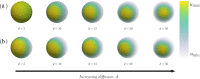
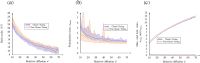
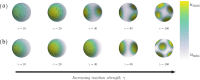
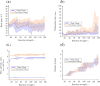
The GTPase Cdc42 is the master regulator of eukaryotic cell polarisation. During this process, the active form of Cdc42 is accumulated at a particular site on the cell membrane called the pole. It is believed that the accumulation of the active Cdc42 resulting in a pole is driven by a combination of activation-inactivation reactions and diffusion. It has been proposed using mathematical modelling that this is the result of diffusion-driven instability, originally proposed by Alan Turing. In this study, we developed, analysed and validated a 3D bulk-surface model of the dynamics of Cdc42. We show that the model can undergo both classic and non-classic Turing instability by deriving necessary conditions for which this occurs and conclude that the non-classic case can be viewed as a limit case of the classic case of diffusion-driven instability. Using three-dimensional Spatio-temporal simulation we predicted pole size and time to polarisation, suggesting that cell polarisation is mainly driven by the reaction strength parameter and that the size of the pole is determined by the relative diffusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
On the influence of cell shape on dynamic reaction-diffusion polarization patterns.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 18;16(3):e0248293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248293. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33735291 Free PMC article.
-
Particle-based simulations of polarity establishment reveal stochastic promotion of Turing pattern formation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Mar 12;14(3):e1006016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006016. eCollection 2018 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 29529021 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern formation in a coupled membrane-bulk reaction-diffusion model for intracellular polarization and oscillations.J Theor Biol. 2020 Jul 21;497:110242. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2020.110242. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Theor Biol. 2020. PMID: 32179107
-
Many roads to symmetry breaking: molecular mechanisms and theoretical models of yeast cell polarity.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Feb 1;28(3):370-380. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-10-0739. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28137950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polarity establishment by Cdc42: Key roles for positive feedback and differential mobility.Small GTPases. 2019 Mar;10(2):130-137. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1275370. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28350208 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational framework for single-cell spatiotemporal dynamics of optogenetic membrane recruitment.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Jul 6;2(7):100245. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100245. eCollection 2022 Jul 18. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 35880018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradshaw, R. A. & Dennis, E. A. Handbook of Cell Signaling (Academic press, 2009).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

