Genetic correlations between traits associated with hyperuricemia, gout, and comorbidities
- PMID: 33637890
- PMCID: PMC8440599
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-021-00830-z
Genetic correlations between traits associated with hyperuricemia, gout, and comorbidities
Abstract
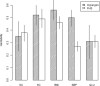
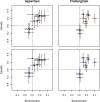
Hypertension, obesity, chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes are comorbidities that have very high prevalence among persons with hyperuricemia (serum urate > 6.8 mg/dL) and gout. Here we use multivariate genetic models to test the hypothesis that the co-association of traits representing hyperuricemia and its comorbidities is genetically based. Using Bayesian whole-genome regression models, we estimated the genetic marker-based variance and the covariance between serum urate, serum creatinine, systolic blood pressure (SBP), blood glucose and body mass index (BMI) from two independent family-based studies: The Framingham Heart Study-FHS and the Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network study-HyperGEN. The main genetic findings that replicated in both FHS and HyperGEN, were (1) creatinine was genetically correlated only with urate and (2) BMI was genetically correlated with urate, SBP, and glucose. The environmental covariance among the traits was generally highest for trait pairs involving BMI. The genetic overlap of traits representing the comorbidities of hyperuricemia and gout appears to cluster in two separate axes of genetic covariance. Because creatinine is genetically correlated with urate but not with metabolic traits, this suggests there is one genetic module of shared loci associated with hyperuricemia and chronic kidney disease. Another module of shared loci may account for the association of hyperuricemia and metabolic syndrome. This study provides a clear quantitative genetic basis for the clustering of comorbidities with hyperuricemia.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to European Society of Human Genetics.
Conflict of interest statement
AIV has received consultant fees from University of Alabama at Birmingham and University of Texas, Austin. JAS has received consultant fees from Crealta/Horizon, Medisys, Fidia, UBM LLC, Trio health, Medscape, WebMD, Clinical Care options, Clearview healthcare partners, Putnam associates, Spherix, Practice Point communications, the National Institutes of Health and the American College of Rheumatology. JAS owns stock options in Amarin pharmaceuticals and Viking therapeutics. JAS is on the speaker’s bureau of Simply Speaking. JAS is a member of the executive of OMERACT, an organization that develops outcome measures in rheumatology and receives arms-length funding from 12 companies. JAS serves on the FDA Arthritis Advisory Committee. JAS is a member of the Veterans Affairs Rheumatology Field Advisory Committee. JAS is the editor and the Director of the UAB Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group Satellite Center on Network Meta-analysis. JAS previously served as a member of the following committees: member, the American College of Rheumatology’s (ACR) Annual Meeting Planning Committee (AMPC) and Quality of Care Committees, the Chair of the ACR Meet-the-Professor, Workshop and Study Group Subcommittee and the co-chair of the ACR Criteria and Response Criteria subcommittee.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL054472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM101219/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR060848/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR060772/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062148/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055673/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

