The default mode network and cognition in Parkinson's disease: A multimodal resting-state network approach
- PMID: 33638213
- PMCID: PMC8090788
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25393
The default mode network and cognition in Parkinson's disease: A multimodal resting-state network approach
Abstract
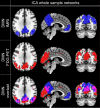
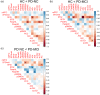
Involvement of the default mode network (DMN) in cognitive symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD) has been reported by resting-state functional MRI (rsfMRI) studies. However, the relation to metabolic measures obtained by [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) is largely unknown. We applied multimodal resting-state network analysis to clarify the association between intrinsic metabolic and functional connectivity abnormalities within the DMN and their significance for cognitive symptoms in PD. PD patients were classified into normal cognition (n = 36) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI; n = 12). The DMN was identified by applying an independent component analysis to FDG-PET and rsfMRI data of a matched subset (16 controls and 16 PD patients) of the total cohort. Besides metabolic activity, metabolic and functional connectivity within the DMN were compared between the patients' groups and healthy controls (n = 16). Glucose metabolism was significantly reduced in all DMN nodes in both patient groups compared to controls, with the lowest uptake in PD-MCI (p < .05). Increased metabolic and functional connectivity along fronto-parietal connections was identified in PD-MCI patients compared to controls and unimpaired patients. Functional connectivity negatively correlated with cognitive composite z-scores in patients (r = -.43, p = .005). The current study clarifies the commonalities of metabolic and hemodynamic measures of brain network activity and their individual significance for cognitive symptoms in PD, highlighting the added value of multimodal resting-state network approaches for identifying prospective biomarkers.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; [18F]-FDG-PET; default mode network; metabolic covariance; mild cognitive impairment; resting-state fMRI.
© 2021 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Amend, M. , Ionescu, T. M. , Di, X. , Pichler, B. J. , Biswal, B. B. , & Wehrl, H. F. (2019). Functional resting‐state brain connectivity is accompanied by dynamic correlations of application‐dependent 18FFDG PET‐tracer fluctuations. NeuroImage, 196, 161–172. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.04.034 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aschenbrenner, S. , Tucha, O. , & Lange, K. W. (2001). RWT Regensburger Wortflüssigkeitstest. Göttingen: Hogrefe Verlag für Psychologie.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

