MicroRNA Mimics or Inhibitors as Antiviral Therapeutic Approaches Against COVID-19
- PMID: 33638807
- PMCID: PMC7910799
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-021-01474-5
MicroRNA Mimics or Inhibitors as Antiviral Therapeutic Approaches Against COVID-19
Abstract
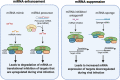
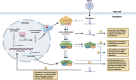
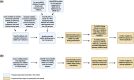
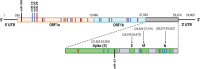
Coronaviruses, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) responsible for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, present a significant threat to human health by inflicting a wide variety of health complications and even death. While conventional therapeutics often involve administering small molecules to fight viral infections, small non-coding RNA sequences, known as microRNAs (miRNAs/miR-), may present a novel antiviral strategy. We can take advantage of their ability to modulate host-virus interactions through mediating RNA degradation or translational inhibition. Investigations into miRNA and SARS-CoV-2 interactions can reveal novel therapeutic approaches against this virus. The viral genomes of SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) were searched using the Nucleotide Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLASTn) for highly similar sequences, to identify potential binding sites for miRNAs hypothesized to play a role in SARS-CoV-2 infection. miRNAs that target angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the receptor used by SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV for host cell entry, were also predicted. Several relevant miRNAs were identified, and their potential roles in regulating SARS-CoV-2 infections were further assessed. Current treatment options for SARS-CoV-2 are limited and have not generated sufficient evidence on safety and efficacy for treating COVID-19. Therefore, by investigating the interactions between miRNAs and SARS-CoV-2, miRNA-based antiviral therapies, including miRNA mimics and inhibitors, may be developed as an alternative strategy to fight COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors, Christine Hum, Julia Loiselle, Nadine Ahmed, Tyler Shaw, Caroline Toudic, and John Paul Pezacki, have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Comment in
-
Comment on: "MicroRNA Mimics or Inhibitors as Antiviral Therapeutic Approaches Against COVID-19".Drugs. 2021 Sep;81(14):1691-1692. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01582-2. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34453690 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhong NS, Zheng BJ, Li YM, Poon LLM, Xie ZH, Chan KH, Li PH, Tan SY, Chang Q, Xie JP, Liu XQ. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People's Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet. 2003;362(9393):1353–1358. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14630-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

