Physical confinement during cancer cell migration triggers therapeutic resistance and cancer stem cell-like behavior
- PMID: 33639204
- PMCID: PMC8112468
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.01.020
Physical confinement during cancer cell migration triggers therapeutic resistance and cancer stem cell-like behavior
Abstract
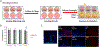
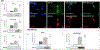
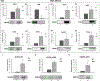
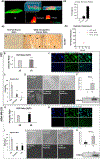
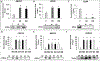
Metastasized cancer cells have an increased resistance to therapies leading to a drastic decrease in patient survival rates. However, our understanding of the cause for this enhanced resistance is lacking. In this study, we report that physically tight confinement during cancer cell migration triggers therapeutic resistance and induces cancer stem cell-like behavior including up-regulation in efflux proteins and in cancer stem cell related markers. Moreover, the re-localization of Yes-associated protein (YAP) to the cell nucleus indicated an elevated level of cytoskeletal tension. The increased cytoskeletal tension suggested that mechanical interactions between cancer cells and tight surroundings during metastasis is one of the factors that contributes to therapeutic resistance and acquisition of cancer stem cell (CSC) like features. With this system and supporting data, we are able to study cells with therapeutic resistance and CSC-like properties for the future purpose of developing new strategies for the treatment of metastatic cancer.
Keywords: Cancer metastasis; Physical confinement; Therapeutic resistance.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
All authors declare that there is no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
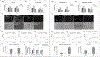
References
-
- Gupta GP, Massagué JJC, Cancer metastasis: building a framework, 127 (2006) 679–695. - PubMed
-
- Friedl P, Wolf K.J.N.r.c., Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms, 3 (2003) 362. - PubMed
-
- M. M, Cellular mechanobiology and cancer metastasis Birth Defects Research Part C: Embryo Today: Reviews, 81 (2007) 329–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

