Bilateral acute renal cortical necrosis after a dog bite: case report
- PMID: 33639872
- PMCID: PMC7913388
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-05901-6
Bilateral acute renal cortical necrosis after a dog bite: case report
Abstract
Background: Capnocytophaga canimorsus is a Gram-negative capnophilic rod and part of dogs/cats' normal oral flora. It can be transmitted by bites, scratches, or even by contact of saliva with injured skin. Asplenic patients and patients with alcohol abuse are at particular risk for fulminant C. canimorsus sepsis. However, also immunocompetent patients can have a severe or even fatal infection. This is the first case of a severe C. canimorsus infection in an immunocompromised host complicated by acute renal cortical necrosis with a "reverse rim sign" in contrast-enhanced computed tomography on hospital admission.
Case presentation: We report the case of a 44-year functionally asplenic patient after an allogeneic stem cell transplantation, who presented with septic shock after a minor dog bite injury 4 days prior. Because of abdominal complaints, epigastric pain with local peritonism, and radiological gallbladder wall thickening, an abdominal focus was suspected after the initial work-up. The patient underwent emergent open cholecystectomy, but the clinical suspicion of abdominal infection was not confirmed. Septic shock was further complicated by cardiomyopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. As a causative pathogen, C. canimorsus could be isolated. The clinical course was complicated by permanent hemodialysis and extensive acral necrosis requiring amputation of several fingers and both thighs.
Conclusion: We present a severe case of a C. canimorsus infection in a functionally asplenic patient after a minor dog bite. The clinical course was complicated by septic shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and the need for multiple amputations. In addition, the rare form of acute renal failure - bilateral acute renal cortical necrosis - was visible as "reverse rim sign" on computed tomography scan. This case is an example of the potential disastrous consequences when omitting pre-emptive antibiotic therapy in wounds inflicted by cats and dogs, particularly in asplenic patients.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Capnocytophaga canimorsus; Case report; Dog bite; Reverse rim sign.
Conflict of interest statement
RS received research grants from the Swiss National Foundation (No 320030_169379), the Research Fund of the University Basel, the Scientific Society Basel, the Gottfried Julia Bangerter-Rhyner Foundation, and UCB-pharma. He received personal grants from UCB-pharma and holds stocks from Alcon, Novartis, Roche, and Johnson & Johnson. The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

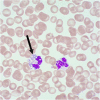
 ); image kindly provided by Health Center Fricktal, Rheinfelden, Switzerland)
); image kindly provided by Health Center Fricktal, Rheinfelden, Switzerland)Similar articles
-
Antibiotic treatment following a dog bite in an immunocompromized patient in order to prevent Capnocytophaga canimorsus infection: a case report.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Jul 5;7:432. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-432. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 24997586 Free PMC article.
-
[Dog bite in a splenectomized patient].Rev Med Liege. 2002 Jan;57(1):40-4. Rev Med Liege. 2002. PMID: 11899497 Review. French.
-
A small 'lick' will sink a great ship: fulminant septicaemia after dog saliva wound treatment in an asplenic patient.Int Wound J. 2017 Dec;14(6):1025-1028. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12752. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Int Wound J. 2017. PMID: 28425162 Free PMC article.
-
An uncommon cause of sepsis following dog exposure.JAAPA. 2021 Jan 1;34(1):1-4. doi: 10.1097/01.JAA.0000723920.24221.1f. JAAPA. 2021. PMID: 33332840
-
[A fatal septic shock due to Capnocytophaga canimorsus and review of literature].Rev Med Interne. 2018 Oct;39(10):820-823. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2018.03.384. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Rev Med Interne. 2018. PMID: 29706238 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Renal abscess with Capnocytophaga canimorsus infection from a dog bite.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 Dec 8;15(12):e250447. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2022-250447. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36593617 Free PMC article.
-
The Great pretender: the first case of septic shock due to Capnocytophaga canimorsus in Sardinia. A Case report and review of the literature.J Public Health Res. 2022 Nov 26;11(4):22799036221133234. doi: 10.1177/22799036221133234. eCollection 2022 Oct. J Public Health Res. 2022. PMID: 36451937 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

