Evaluation of serum levels of C-reactive protein, D-Dimer and Autologous Serum Skin Test in patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria in a Brazilian tertiary center : a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 33640190
- PMCID: PMC8007487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abd.2020.07.006
Evaluation of serum levels of C-reactive protein, D-Dimer and Autologous Serum Skin Test in patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria in a Brazilian tertiary center : a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The pathophysiology of urticaria is still poorly understood. Recent studies demonstrate that the activation of coagulation is correlated with the clinical activity of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria. Coagulation and inflammation are strongly linked.
Objectives: To correlate the severity and activity of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria with the levels of D-dimer, C-reactive protein, and autologous serum test in patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria.
Methods: The study included 55 patients diagnosed with chronic spontaneous urticaria. D-dimer levels were measured using enzyme-linked fluorescent assay and C-reactive protein levels were measured using the nephelometric method; autologous serum testing was performed on patients who discontinued antihistamine therapy. The severity of the disease was assessed using the urticaria activity score.
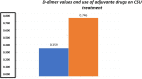
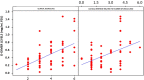
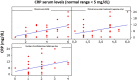
Results: patients with severe, spontaneous, and difficult-to-control chronic urticaria had elevated serum levels of D-dimer, as well as a positive autologous serum test. Little correlation was demonstrated between the severity of chronic spontaneous urticaria and the levels of C-reactive protein.
Conclusion: The authors concluded that patients with severe Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria showed signs of activated fibrinolysis. Most patients with high clinical scores had high D-dimer values. Patients with positive results for the autologous serum test also had more severe Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria and needed more drugs to control the disease. Finally, little correlation was found between C-reactive protein levels and disease severity.
Study limitations: The main limitation was the small sample of patients. In the present patients, it was demonstrated that serum D-dimer levels and the autologous serum test can act as predictive markers of severity and activity of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria.
Keywords: Angioedema; Pharmacological biomarkers; Urticaria.
Copyright © 2021 Sociedade Brasileira de Dermatologia. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bernstein J.A., Lang D.M., Khan D.A., Craig T., Dreyfus D., Hsieh F. The diagnosis and management of acute and chronic urticaria: 2014 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1270–1277. - PubMed
-
- Cugno M., Marzano A.V., Asero R., Tedeschi A. Activation of blood coagulation in chronic urticaria: pathophysiological and clinical implications. Intern Emerg Med. 2010;5:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Asero R., Tedeschi A., Riboldi P., Griffini S., Bonanni E., Cugno M. Severe chronic urticaria is associated with elevated plasma levels of D-dimer. Allergy. 2008;63:176–180. - PubMed
-
- Takahagi S., Mihara S., Iwamoto K., Morioke S., Okabe T., Kameyoshi Y. Coagulation/fibrinolysis and inflammation markers are associated with disease activity in patients with chronic urticaria. Allergy. 2010;65:649–656. - PubMed
-
- Rabelo-Filardi R., Daltro-Oliveira R., Campos R.A. Parameters associated with chronic spontaneous urticaria duration and severity: a systematic review. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;161:197–204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

