Regulation of Promoter Proximal Pausing of RNA Polymerase II in Metazoans
- PMID: 33640324
- PMCID: PMC8184617
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166897
Regulation of Promoter Proximal Pausing of RNA Polymerase II in Metazoans
Abstract
Regulation of transcription is a tightly choreographed process. The establishment of RNA polymerase II promoter proximal pausing soon after transcription initiation and the release of Pol II into productive elongation are key regulatory processes that occur in early elongation. We describe the techniques and tools that have become available for the study of promoter proximal pausing and their utility for future experiments. We then provide an overview of the factors and interactions that govern a multipartite pausing process and address emerging questions surrounding the mechanism of RNA polymerase II's subsequent advancement into the gene body. Finally, we address remaining controversies and future areas of study.
Keywords: DSIF; NELF; P-TEFb; Pol II; TFIID.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
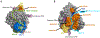
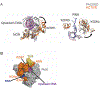
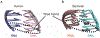


References
-
- Bentley DL, Groudine M. (1986) A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 321:702–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

