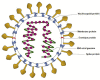
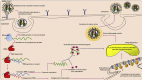
Exploring algae and cyanobacteria as a promising natural source of antiviral drug against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33640332
- PMCID: PMC7836382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.11.014
Exploring algae and cyanobacteria as a promising natural source of antiviral drug against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
The present outburst of coronavirus-associated (SARS-CoV-2) acute respiratory disease coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) in December 2019 in Wuhan, China is the third recognised spill over due to the zoonotic transmission. SARS-CoVs are about 29.7 kb positive, single stranded (ss) RNA viruses that are considered as zoonotic pathogens, bat being their natural reservoirs and also shows transmission within humans. The rapidly increasing COVID-19 cases and need of best and efficient drug/vaccine/strategy to counteract the virus entry and its pathogenesis has made it a Herculean challenge for scientists. Synthetic drugs associated complications has attracted scientific attention for natural product-based drugs. Chemo-diversity of algae and cyanobacteria offers a novel approach and can be recognized as a relevant source for developing a future natural "antiviral drug". The aim of this review is to highlight important features of SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 and the antiviral compounds recognized in algae and cyanobacteria, with their mechanisms of actions. Algae possess both immunity improving capacity and suppresses many viruses. Thus, they can be recommended as a preventive and curative remedy against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; Algal compounds; Coronavirus.
Copyright © 2020 Chang Gung University. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. No conflicts, informed consent, or human or animal rights are applicable to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Algae-Derived Bioactive Molecules for the Potential Treatment of SARS-CoV-2.Molecules. 2021 Apr 8;26(8):2134. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082134. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33917694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyanobacterial natural products as sources for antiviral drug discovery against COVID-19.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Oct;40(16):7629-7644. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1899050. Epub 2021 Mar 22. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33749496 Review.
-
Marine sulfated polysaccharides as potential antiviral drug candidates to treat Corona Virus disease (COVID-19).Carbohydr Res. 2021 Jul;505:108326. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108326. Epub 2021 May 3. Carbohydr Res. 2021. PMID: 34015720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory activities of marine sulfated polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2.Food Funct. 2020 Sep 23;11(9):7415-7420. doi: 10.1039/d0fo02017f. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32966484
-
Can algae contribute to the war with Covid-19?Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):1226-1237. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1910432. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33858291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Multifaceted Computational Approach to Understanding the MERS-CoV Main Protease and Brown Algae Compounds' Interaction.Mar Drugs. 2023 Nov 30;21(12):626. doi: 10.3390/md21120626. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 38132947 Free PMC article.
-
Recent development of oral vaccines (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2024 Mar 22;27(5):223. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12511. eCollection 2024 May. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38590568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyanometabolites: molecules with immense antiviral potential.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Apr 3;205(5):164. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03514-y. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37012452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microalgae as an Efficient Vehicle for the Production and Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Glycoproteins against SARS-CoV-2 Variants.Mar Drugs. 2022 Oct 23;20(11):657. doi: 10.3390/md20110657. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36354980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review on algal nutraceuticals as prospective therapeutic agent for different diseases.3 Biotech. 2023 Feb;13(2):44. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03454-2. Epub 2023 Jan 11. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 36643398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it.https://www.canaryhealthtech.com/news/naming-the-coronavirusdisease-covi...
-
- Carossino M., Thiry E., de la Grandière A., Barrandeguy M.E. Novel vaccination approaches against equine alphavirus encephalitides. Vaccine. 2014;3:311–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous