Direct Measurement of ATP7B Peptides Is Highly Effective in the Diagnosis of Wilson Disease
- PMID: 33640437
- PMCID: PMC8243898
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.052
Direct Measurement of ATP7B Peptides Is Highly Effective in the Diagnosis of Wilson Disease
Abstract
Background & aims: Both existing clinical criteria and genetic testing have significant limitations for the diagnosis of Wilson disease (WD), often creating ambiguities in patient identification and leading to delayed diagnosis and ineffective management. ATP7B protein concentration, indicated by direct measurement of surrogate peptides from patient dried blood spot samples, could provide primary evidence of WD. ATP7B concentrations were measured in patient samples from diverse backgrounds, diagnostic potential is determined, and results are compared with biochemical and genetic results from individual patients.
Methods: Two hundred and sixty-four samples from biorepositories at 3 international and 2 domestic academic centers and 150 normal controls were obtained after Institutional Review Board approval. Genetically or clinically confirmed WD patients with a Leipzig score >3 and obligate heterozygote (carriers) from affected family members were included. ATP7B peptide measurements were made by immunoaffinity enrichment mass spectrometry.
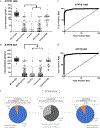
Results: Two ATP7B peptides were used to measure ATP7B protein concentration. Receiver operating characteristics curve analysis generates an area under the curve of 0.98. ATP7B peptide analysis of the sequence ATP7B 887 was found to have a sensitivity of 91.2%, specificity of 98.1%, positive predictive value of 98.0%, and a negative predictive value of 91.5%. In patients with normal ceruloplasmin concentrations (>20 mg/dL), 14 of 16 (87.5%) were ATP7B-deficient. In patients without clear genetic results, 94% were ATP7B-deficient.
Conclusions: Quantification of ATP7B peptide effectively identified WD patients in 92.1% of presented cases and reduced ambiguities resulting from ceruloplasmin and genetic analysis. Clarity is brought to patients with ambiguous genetic results, significantly aiding in noninvasive diagnosis. A proposed diagnostic score and algorithm incorporating ATP7B peptide concentrations can be rapidly diagnostic and supplemental to current Leipzig scoring systems.
Keywords: ATP7B; Immuno-SRM; Leipzig Score; Wilson disease.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Expanding the Diagnostic Toolkit of Wilson Disease with ATP7B Peptides.Gastroenterology. 2021 Jun;160(7):2249-2251. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.025. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 33753100 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bull PC, Thomas GR, Rommens JM, et al. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet 1993;5:327–37. - PubMed
-
- Terada K, Schilsky ML, Miura N, et al. ATP7B (WND) protein. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1998;30:1063–7. - PubMed
-
- Hahn SH. Population screening for Wilson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2014;1315:64–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

