A review of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater and airborne particulates and its use for virus spreading surveillance
- PMID: 33640498
- PMCID: PMC7906514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110929
A review of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater and airborne particulates and its use for virus spreading surveillance
Abstract
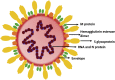
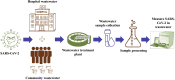
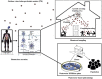
According to the WHO, on October 16, 2020, the spreading of the SARS-CoV-2, responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, reached 235 countries and territories, and resulting in more than 39 million confirmed cases and 1.09 million deaths globally. Monitoring of the virus outbreak is one of the main activities pursued to limiting the number of infected people and decreasing the number of deaths that have caused high pressure on the health care, social, and economic systems of different countries. Wastewater based epidemiology (WBE), already adopted for the surveillance of life style and health conditions of communities, shows interesting features for the monitoring of the COVID-19 diffusion. Together with wastewater, the analysis of airborne particles has been recently suggested as another useful tool for detecting the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in given areas. The present review reports the status of research currently performed concerning the monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 spreading by WBE and airborne particles. The former have been more investigated, whereas the latter is still at a very early stage, with a limited number of very recent studies. Nevertheless, the main results highlights in both cases necessitate more research activity for better understating and defining the biomarkers and the related sampling and analysis procedures to be used for this important aim.
Keywords: Airborne particles; Biomarkers; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Wastewater; Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE).
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Adelodun B., Ajibade F.O., Ibrahim R.G., Bakare H.O., Choi K.-S. Snowballing transmission of COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) through wastewater: any sustainable preventive measures to curtail the scourge in low-income countries? Sci. Total Environ. 2020;742 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140680. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adelodun B., Ajibade F.O., Ighalo J.O., Odey G., Ibrahim R.G., Kareem K.Y., Bakare H.O., Tiamiyu A.O., Ajibade T.F., Abdulkadir S.T., Adeniran K.A., Choi K.S. Assessment of socioeconomic inequality based on virus-contaminated water usage in developing countries: a review. Environ. Res. 2020;192 doi: 10.1016/j.envre.2020.110309. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed W., Angel N., Edson J., Bibby K., Bivins A., O'Brien J.W., Choi P.M., Kitajima M., Simpson S.L., Li J., Tscharke B., Verhagen R., Smith W.J.M., Zaugg J., Dierens L., Hugenholtz P., Thomas K.V., Mueller J.F. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;728 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed W., Bertsch P.M., Angel N., Bibby K., Bivins A., Dierens L., Edson J., Ehret J., Gyawali P., Hamilton K.A., Hosegood I., Hugenholtz P., Jiang G., Kitajima M., Sichani H.T., Shi J., Shimko K.M., Simpson S.L., Smith W.J.M., Symonds E.M., Thomas K.V., Verhagen R., Zaugg J., Mueller J.F. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in commercial passenger aircraft and cruise ship wastewater: a surveillance tool for assessing the presence of COVID-19 infected travellers. J. Travel Med. 2020;27:1–11. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taaa116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous