Identification of proteins and cellular pathways targeted by 2-nitroimidazole hypoxic cytotoxins
- PMID: 33640700
- PMCID: PMC7933538
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101905
Identification of proteins and cellular pathways targeted by 2-nitroimidazole hypoxic cytotoxins
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to 'Identification of proteins and cellular pathways targeted by 2-nitroimidazole hypoxic cytotoxins' [Redox Biol. 41 (2021) 101905].Redox Biol. 2021 Aug;44:101986. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101986. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Redox Biol. 2021. PMID: 33910780 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
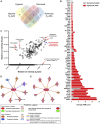
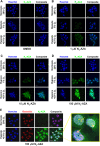
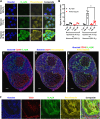
Tumour hypoxia negatively impacts therapy outcomes and continues to be a major unsolved clinical problem. Nitroimidazoles are hypoxia selective compounds that become entrapped in hypoxic cells by forming drug-protein adducts. They are widely used as hypoxia diagnostics and have also shown promise as hypoxia-directed therapeutics. However, little is known about the protein targets of nitroimidazoles and the resulting effects of their modification on cancer cells. Here, we report the synthesis and applications of azidoazomycin arabinofuranoside (N3-AZA), a novel click-chemistry compatible 2-nitroimidazole, designed to facilitate (a) the LC-MS/MS-based proteomic analysis of 2-nitroimidazole targeted proteins in FaDu head and neck cancer cells, and (b) rapid and efficient labelling of hypoxic cells and tissues. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that many of the 62 target proteins we identified participate in key canonical pathways including glycolysis and HIF1A signaling that play critical roles in the cellular response to hypoxia. Critical cellular proteins such as the glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and the detoxification enzyme glutathione S-transferase P (GSTP1) appeared as top hits, and N3-AZA adduct formation significantly reduced their enzymatic activities only under hypoxia. Therefore, GAPDH, GSTP1 and other proteins reported here may represent candidate targets to further enhance the potential for nitroimidazole-based cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: Click chemistry; Head and neck tumour; Hypoxia; Nitroimidazole; Proteomics.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Michael Weinfeld, Piyush Kumar and Hassan El-Saidi are included in the following patent application: Markers, conjugates, compositions and methods for hypoxia imaging, mapping, and therapy. International PCT Patent, Application No. PCT/CA2018/051165. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Janssen H., Haustermans K., Balm A., Begg A. Hypoxia in head and neck cancer: how much, how important? Head Neck. 2005;27:622–638. - PubMed
-
- House S.W., Warburg O., Burk D., Schade A.L. On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science. 1956;124:267–272. - PubMed
-
- Kumareswaran R., Ludkovski O., Meng A., Sykes J., Pintilie M., Bristow R.G. Chronic hypoxia compromises repair of DNA double-strand breaks to drive genetic instability. J. Cell Sci. 2012;125:189–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

