Neuroprotective effect of hydrogen sulfide against glutamate-induced oxidative stress is mediated via the p53/glutaminase 2 pathway after traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 33640879
- PMCID: PMC7993660
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202575
Neuroprotective effect of hydrogen sulfide against glutamate-induced oxidative stress is mediated via the p53/glutaminase 2 pathway after traumatic brain injury
Abstract
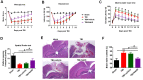
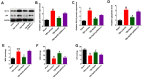
Several reports suggest that hydrogen sulfide (H2S) exerts multiple biological and physiological effects on the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury (TBI). However, the exact molecular mechanism involved in this effect is not yet fully known. In this study, we found that H2S alleviated TBI-induced motor and spatial memory deficits, brain pathology, and brain edema. Moreover, sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS), an H2S donor, treatment markedly increased the expression of Bcl-2, while inhibited the expression of Bax and Cleaved caspase-3 in TBI-challenged rats. Tunnel staining also demonstrated these results. Treatment with NaHS significantly reduced the glutamate and glutaminase 2 (GLS-2) protein levels, and glutamate-mediated oxidative stress in TBI-challenged rats. Furthermore, we demonstrated that H2S treatment inhibited glutamate-mediated oxidative stress through the p53/GLS-2 pathway. Therefore, our results suggested that H2S protects brain injury induced by TBI through modulation of the glutamate-mediated oxidative stress in the p53/GLS-2 pathway-dependent manner.
Keywords: glutamate; hydrogen sulfide; oxidative stress; p53; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
NaHS alters synaptic plasticity proteins and enhances dendritic arborization to improve cognitive and motor deficits after traumatic brain injury in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;182(5):1183-1205. doi: 10.1111/bph.17386. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39562524
-
The protective effect of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) on traumatic brain injury (TBI) induced memory deficits in rats.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Sep;134:177-182. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.07.014. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 28739248
-
Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide in a rat model of traumatic brain injury via activation of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels and reduction of oxidative stress.J Surg Res. 2013 Oct;184(2):e27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.03.067. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23590867
-
Hydrogen sulfide and its donors for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: A comprehensive review.Int J Pharm. 2025 Jul 25;680:125792. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125792. Epub 2025 May 28. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40446877 Review.
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Localization and Structural-Functional Organization of p53 Following Traumatic Brain Injury: Development of a YOLO Model for Detection and Quantification of Apoptotic Nuclei.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 24;26(11):5066. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115066. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507878 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Regulation of Cell Death following Neurotrauma and Related Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10742. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310742. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide alleviates neural degeneration probably by reducing oxidative stress and aldose reductase expression.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Nov;28(21):e70192. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70192. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39517099 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide to repair cardiovascular injury after trauma.Nitric Oxide. 2022 Dec 1;129:82-101. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Nitric Oxide. 2022. PMID: 36280191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide in Alzheimer's Disease and Traumatic Brain Injury.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 13;12(5):1095. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051095. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

