DPYD, down-regulated by the potentially chemopreventive agent luteolin, interacts with STAT3 in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 33640964
- PMCID: PMC8283735
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgab017
DPYD, down-regulated by the potentially chemopreventive agent luteolin, interacts with STAT3 in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
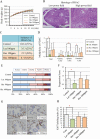
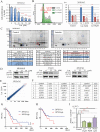
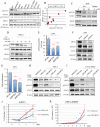
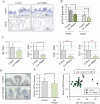
The 5-year survival rate of pancreatic ductal carcinoma (PDAC) patients is <10% despite progress in clinical medicine. Strategies to prevent the development of PDAC are urgently required. The flavonoids Luteolin (Lut) and hesperetin (Hes) may be cancer-chemopreventive, but effects on pancreatic carcinogenesis in vivo have not been studied. Here, the chemopreventive effects of Lut and Hes on pancreatic carcinogenesis are assessed in the BOP-induced hamster PDAC model. Lut but not Hes suppressed proliferation of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) and reduced the incidence and multiplicity of PDAC in this model. Lut also inhibited the proliferation of hamster and human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Multi-blot and microarray assays revealed decreased phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) on Lut exposure. To explore the relationship between DPYD and STAT3 activity, the former was silenced by RNAi or overexpressed using expression vectors, and the latter was inactivated by small molecule inhibitors or stimulated by IL6 in human PDAC cells. DPYD knock-down decreased, and overexpression increased, pSTAT3 and cell proliferation. DPYD expression was decreased by inactivation of STAT3 and increased by its activation. The frequency of pSTAT3-positive cells and DPYD expression was significantly correlated and was decreased in parallel by Lut in the hamster PDAC model. Finally, immunohistochemical analysis in 73 cases of human PDAC demonstrated that DPYD expression was positively correlated with the Ki-67 labeling index, and high expression was associated with poor prognosis. These results indicate that Lut is a promising chemopreventive agent for PDAC, targeting a novel STAT3-DPYD pathway.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. (2017) Vital Statistics Japan.
-
- Benzel, J., et al. (2018) Chemoprevention and treatment of pancreatic cancer: update and review of the literature. Digestion, 97, 275–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

