Tissue Doppler Imaging (E/e') and Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure in Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis
- PMID: 33642168
- PMCID: PMC8076064
- DOI: 10.1053/j.jvca.2021.01.051
Tissue Doppler Imaging (E/e') and Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure in Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis
Abstract
Objective: Although American and European consensus statements advocate using the ratio of the transmitral E velocity and tissue Doppler early diastolic mitral annular velocity (E/e') in the assessment of left-sided heart filling pressures, recent reports have questioned the reliability of this ratio to predict left atrial pressures in a variety of disease states. The authors hypothesized that there is a clinically significant correlation between E/e' and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) in patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Participants: The study comprised 733 consecutive patients with severe aortic stenosis who underwent transcatheter aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis.
Interventions: None.
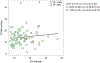
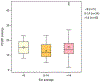
Measurements and main results: PCWP and E/e'ave (average of the lateral and medial annulus tissue Doppler velocities) were measured with a pulmonary artery catheter and transthoracic echocardiography during preprocedural evaluation. Patients were grouped by left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥50% and LVEF <50%. Spearman rank correlation, analysis of variance, and t and chi-square tests were used to analyze the data. Seventy-nine patients met the inclusion criteria. There was no significant correlation between E/e'ave and PCWP (n = 79, Spearman r = 0.096; p = 0.3994). This correlation did not improve when ventricular function was considered (LVEF <50%: n = 11, Spearman r = -0.097; p = 0.776 and LVEF ≥50%: n = 68, Spearman r = 0.116; p = 0.345). There was no statistically significant difference in mean PCWP between each range of E/e'ave.
Conclusion: A clinically relevant relationship between E/e' and PCWP was not observed in patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Keywords: E/e’; TAVR; aortic stenosis; diastology; echocardiography; pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; tissue Doppler; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report.
Figures


References
-
- Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. European heart journal cardiovascular Imaging. 2016;17(12):1321–1360. - PubMed
-
- Nagueh SF, Middleton KJ, Kopelen HA, Zoghbi WA, Quinones MA. Doppler tissue imaging: a noninvasive technique for evaluation of left ventricular relaxation and estimation of filling pressures. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 1997;30(6):1527–1533. - PubMed
-
- Sundereswaran L, Nagueh SF, Vardan S, et al. Estimation of left and right ventricular filling pressures after heart transplantation by tissue Doppler imaging. The American journal of cardiology. 1998;82(3):352–357. - PubMed
-
- Nagueh SF, Mikati I, Kopelen HA, Middleton KJ, Quinones MA, Zoghbi WA. Doppler estimation of left ventricular filling pressure in sinus tachycardia. A new application of tissue doppler imaging. Circulation. 1998;98(16):1644–1650. - PubMed
-
- Nagueh SF, Lakkis NM, Middleton KJ, Spencer WH 3rd, Zoghbi WA, Quinones MA. Doppler estimation of left ventricular filling pressures in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1999;99(2):254–261. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

