Efficacy of non-invasive diagnostic methods in the diagnosis and screening of oral cancer and precancer
- PMID: 33642212
- PMCID: PMC9615541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.12.019
Efficacy of non-invasive diagnostic methods in the diagnosis and screening of oral cancer and precancer
Abstract
Introduction: Traditional meta-analyses on the diagnostic accuracy of oral lesions have been conducted, but they were inherently limited to direct pairwise comparisons between a single method and a single alternative, while multiple diagnostic options and the ranking thereof were methodologically not possible.
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic values of various methods in patients with oral potential malignant disease by performing a network meta-analysis.
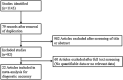
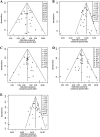
Methods: Two authors independently searched the databases (MEDLINE, SCOPUS, the Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials, and Google scholar) up to June 2020 for studies comparing the diagnostic accuracy of various tools (autofluorescence, chemiluminescence, cytology, narrow band imaging, and toluidine blue) with visual examination or other tools. The outcomes of interest for this analysis were sensitivity, specificity, negative predictive value, positive predictive value and accuracy. Both a standard pairwise meta-analysis and network meta-analysis were conducted.
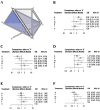
Results: Treatment networks consisting of six interventions were defined for the network meta-analysis. The results of traditional meta-analysis showed that, among six methods, narrow band imaging showed higher sensitivity, specificity, negative predictive value, positive predictive value, and accuracy compared to visual examination. The results of network meta-analysis showed that autofluorescence, chemiluminescence, and narrow band imaging had higher sensitivity compared with visual examination, and that chemiluminescence and narrow band imaging had higher negative predictive value compared with visual examination. However, autofluorescence and chemiluminescence had lower specificity compared with visual examination. There were no significant differences in positive predictive value and accuracy among the six interventions.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that narrow banding imaging has superiority in terms of sensitivity and negative predictive value compared with the other five tested agents.
Keywords: Autofluorescence; Chemiluminescence; Mouth neoplasms; Narrow band imaging; Tolonium chloride.
Copyright © 2021 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang L., Williams M., Poh C.F., Laronde D., Epstein J.B., Durham S., et al. Toluidine blue staining identifies high-risk primary oral premalignant lesions with poor outcome. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8017–8021. - PubMed
-
- Rahman F., Tippu S.R., Khandelwal S., Girish K.L., Manjunath B.C., Bhargava A. A study to evaluate the efficacy of toluidine blue and cytology in detecting oral cancer and dysplastic lesions. Quintessence Int. 2012;43:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Awan K., Yang Y., Morgan P., Warnakulasuriya S. Utility of toluidine blue as a diagnostic adjunct in the detection of potentially malignant disorders of the oral cavity – a clinical and histological assessment. Oral Dis. 2012;18:728–733. - PubMed
-
- Thomson P.J. Field change and oral cancer: new evidence for widespread carcinogenesis? Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;31:262–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

