Cannabinoids in Audiogenic Seizures: From Neuronal Networks to Future Perspectives for Epilepsy Treatment
- PMID: 33643007
- PMCID: PMC7904685
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.611902
Cannabinoids in Audiogenic Seizures: From Neuronal Networks to Future Perspectives for Epilepsy Treatment
Abstract
Cannabinoids and Cannabis-derived compounds have been receiving especial attention in the epilepsy research scenario. Pharmacological modulation of endocannabinoid system's components, like cannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1R) and their bindings, are associated with seizures in preclinical models. CB1R expression and functionality were altered in humans and preclinical models of seizures. Additionally, Cannabis-derived compounds, like cannabidiol (CBD), present anticonvulsant activity in humans and in a great variety of animal models. Audiogenic seizures (AS) are induced in genetically susceptible animals by high-intensity sound stimulation. Audiogenic strains, like the Genetically Epilepsy Prone Rats, Wistar Audiogenic Rats, and Krushinsky-Molodkina, are useful tools to study epilepsy. In audiogenic susceptible animals, acute acoustic stimulation induces brainstem-dependent wild running and tonic-clonic seizures. However, during the chronic protocol of AS, the audiogenic kindling (AuK), limbic and cortical structures are recruited, and the initially brainstem-dependent seizures give rise to limbic seizures. The present study reviewed the effects of pharmacological modulation of the endocannabinoid system in audiogenic seizure susceptibility and expression. The effects of Cannabis-derived compounds in audiogenic seizures were also reviewed, with especial attention to CBD. CB1R activation, as well Cannabis-derived compounds, induced anticonvulsant effects against audiogenic seizures, but the effects of cannabinoids modulation and Cannabis-derived compounds still need to be verified in chronic audiogenic seizures. The effects of cannabinoids and Cannabis-derived compounds should be further investigated not only in audiogenic seizures, but also in epilepsy related comorbidities present in audiogenic strains, like anxiety, and depression.
Keywords: CB1 receptors; Cannabis-derived compounds; audiogenic seizures; cannabidiol; endocannabinoid system; epilepsy; genetically-developed strains; neuronal networks.
Copyright © 2021 Lazarini-Lopes, Do Val-da Silva, da Silva-Júnior, Cunha and Garcia-Cairasco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

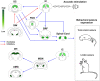
Similar articles
-
Cannabidiol attenuates generalized tonic-clonic and suppresses limbic seizures in the genetically epilepsy-prone rats (GEPR-3) strain.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Feb;75(1):166-176. doi: 10.1007/s43440-022-00416-6. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36195689 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic cannabidiol (CBD) administration induces anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic effects in a genetic model of epilepsy.Epilepsy Behav. 2021 Jun;119:107962. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107962. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Epilepsy Behav. 2021. PMID: 33887676
-
Neuroethological and morphological (Neo-Timm staining) correlates of limbic recruitment during the development of audiogenic kindling in seizure susceptible Wistar rats.Epilepsy Res. 1996 Dec;26(1):177-92. doi: 10.1016/s0920-1211(96)00050-2. Epilepsy Res. 1996. PMID: 8985699
-
Therapeutic effects of cannabinoids in animal models of seizures, epilepsy, epileptogenesis, and epilepsy-related neuroprotection.Epilepsy Behav. 2017 May;70(Pt B):319-327. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.11.006. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Epilepsy Behav. 2017. PMID: 28190698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR) strain and its contributions to epileptology and related comorbidities: History and perspectives.Epilepsy Behav. 2017 Jun;71(Pt B):250-273. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 May 11. Epilepsy Behav. 2017. PMID: 28506440 Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabidiol attenuates generalized tonic-clonic and suppresses limbic seizures in the genetically epilepsy-prone rats (GEPR-3) strain.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Feb;75(1):166-176. doi: 10.1007/s43440-022-00416-6. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36195689 Free PMC article.
-
A complex systems view on the current hypotheses of epilepsy pharmacoresistance.Epilepsia Open. 2022 Aug;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S8-S22. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12588. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Epilepsia Open. 2022. PMID: 35253410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CBGA ameliorates inflammation and fibrosis in nephropathy.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 18;13(1):6341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33507-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37072467 Free PMC article.
-
Use of cannabidiol in the treatment of drug-refractory epilepsy in children and young adults: A systematic review.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2024 Apr-Jun;15(2):203-210. doi: 10.25259/JNRP_618_2023. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2024. PMID: 38746511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabigerolic Acid (CBGA) Inhibits the TRPM7 Ion Channel Through its Kinase Domain.Function (Oxf). 2023 Dec 7;5(1):zqad069. doi: 10.1093/function/zqad069. eCollection 2024. Function (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 38162115 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

