Neurobehavioral Correlates of Surprisal in Language Comprehension: A Neurocomputational Model
- PMID: 33643143
- PMCID: PMC7905034
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.615538
Neurobehavioral Correlates of Surprisal in Language Comprehension: A Neurocomputational Model
Abstract
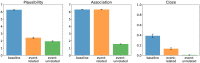
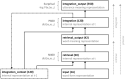
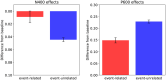
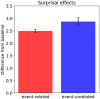
Expectation-based theories of language comprehension, in particular Surprisal Theory, go a long way in accounting for the behavioral correlates of word-by-word processing difficulty, such as reading times. An open question, however, is in which component(s) of the Event-Related brain Potential (ERP) signal Surprisal is reflected, and how these electrophysiological correlates relate to behavioral processing indices. Here, we address this question by instantiating an explicit neurocomputational model of incremental, word-by-word language comprehension that produces estimates of the N400 and the P600-the two most salient ERP components for language processing-as well as estimates of "comprehension-centric" Surprisal for each word in a sentence. We derive model predictions for a recent experimental design that directly investigates "world-knowledge"-induced Surprisal. By relating these predictions to both empirical electrophysiological and behavioral results, we establish a close link between Surprisal, as indexed by reading times, and the P600 component of the ERP signal. The resultant model thus offers an integrated neurobehavioral account of processing difficulty in language comprehension.
Keywords: N400; P600; event-related potentials (ERPs); language comprehension; surprisal theory.
Copyright © 2021 Brouwer, Delogu, Venhuizen and Crocker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
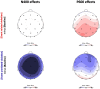
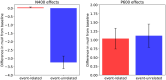
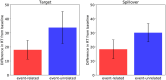
References
-
- Albrecht J. E., O'Brien E. J. (1993). Updating a mental model: maintaining both local and global coherence. J. Exp. Psychol. 19, 1061–1070. 10.1037/0278-7393.19.5.1061 - DOI
-
- Bates D., Kliegl R., Vasishth S., Baayen H. (2015). Parsimonious mixed models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.04967. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.04967
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

