Alteration of Gut Microbiota After Antibiotic Exposure in Finishing Swine
- PMID: 33643231
- PMCID: PMC7906994
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.596002
Alteration of Gut Microbiota After Antibiotic Exposure in Finishing Swine
Abstract
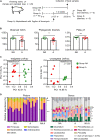
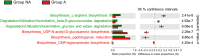
Subclinical doses of antimicrobials are commonly used in the swine industry to control infectious diseases and growth performance. Accumulating evidence suggests that swine administered with antibiotics are susceptible to disease development due to disruption of the beneficial gut microbial community, which is associated with host immune regulation, nutrient digestion, and colonization resistance against pathogens. In this study, we found that finishing swine administered with lincomycin showed gut dysbiosis and increased diarrhea incidence compared with control swine. 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing was used to analyze the gut microbiota in finishing swine administered with lincomycin. The relative abundance of detrimental microbes, such as species of Clostridium, Aerococcus, Escherichia-Shigella, and Corynebacterium was increased in the feces of lincomycin-administered finishing swine, but that of bacteria associated with fiber degradation, such as species of Treponema, Succinivibrio, Fibrobacter, and Cellulosilyticum was decreased. Moreover, administration of lincomycin significantly increased the enrichment of metabolic pathways related to pathogenicity and deficiency of polysaccharide degradation. These results suggest that lincomycin treatment could cause severe disruption of the commensal microbiota in finishing swine.
Keywords: antimicrobial; fecal microbiome; gut dysfunction; meta-analysis; swine.
Copyright © 2021 Jo, Kwon, Whon, Kim, Yun, Lee, Shin, Kim and Choi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Costa K. A., Soares A. D., Wanner S. P., Santos R., Fernandes S. O., Martins Fdos S., et al. (2014). L-arginine supplementation prevents increases in intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation in male Swiss mice subjected to physical exercise under environmental heat stress. J. Nutr. 144 218–223. 10.3945/jn.113.183186 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

