Transcriptomic Analysis of Wheat Seedling Responses to the Systemic Acquired Resistance Inducer N-Hydroxypipecolic Acid
- PMID: 33643249
- PMCID: PMC7905219
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.621336
Transcriptomic Analysis of Wheat Seedling Responses to the Systemic Acquired Resistance Inducer N-Hydroxypipecolic Acid
Abstract
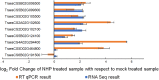
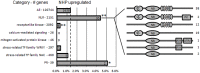
The fungal pathogen Fusarium graminearum can cause destructive diseases on wheat, such as Fusarium head blight and Fusarium crown rot. However, a solution is still unavailable. Recently, N-hydroxypipecolic acid (NHP) was identified as a potent signaling molecule that is capable of inducing systemic acquired resistance to bacterial, oomycete, and fungal infection in several plant species. However, it is not clear whether NHP works in wheat to resist F. graminearum infection or how NHP affects wheat gene expression. In this report, we showed that pretreatment with NHP moderately increased wheat seedling resistance to F. graminearum. Using RNA sequencing, we found that 17% of wheat-expressed genes were significantly affected by NHP treatment. The genes encoding nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat immune receptors were significantly overrepresented in the group of genes upregulated by NHP treatment, while the genes encoding receptor-like kinases were not. Our results suggested that NHP treatment sensitizes a subset of the immune surveillance system in wheat seedlings, thereby facilitating wheat defense against F. graminearum infection.
Keywords: Fusarium head blight (FHB); fungal infection; immune receptor; pathogen; systemic acquired resistance; wheat.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Zhang and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B 57 289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

