The Trinity of cGAS, TLR9, and ALRs Guardians of the Cellular Galaxy Against Host-Derived Self-DNA
- PMID: 33643304
- PMCID: PMC7905024
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.624597
The Trinity of cGAS, TLR9, and ALRs Guardians of the Cellular Galaxy Against Host-Derived Self-DNA
Abstract
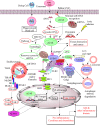
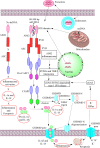
The immune system has evolved to protect the host from the pathogens and allergens surrounding their environment. The immune system develops in such a way to recognize self and non-self and develops self-tolerance against self-proteins, nucleic acids, and other larger molecules. However, the broken immunological self-tolerance leads to the development of autoimmune or autoinflammatory diseases. Pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) are expressed by immunological cells on their cell membrane and in the cytosol. Different Toll-like receptors (TLRs), Nod-like receptors (NLRs) and absent in melanoma-2 (AIM-2)-like receptors (ALRs) forming inflammasomes in the cytosol, RIG (retinoic acid-inducible gene)-1-like receptors (RLRs), and C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) are some of the PRRs. The DNA-sensing receptor cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is another PRR present in the cytosol and the nucleus. The present review describes the role of ALRs (AIM2), TLR9, and cGAS in recognizing the host cell DNA as a potent damage/danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP), which moves out to the cytosol from its housing organelles (nucleus and mitochondria). The introduction opens with the concept that the immune system has evolved to recognize pathogens, the idea of horror autotoxicus, and its failure due to the emergence of autoimmune diseases (ADs), and the discovery of PRRs revolutionizing immunology. The second section describes the cGAS-STING signaling pathway mediated cytosolic self-DNA recognition, its evolution, characteristics of self-DNAs activating it, and its role in different inflammatory conditions. The third section describes the role of TLR9 in recognizing self-DNA in the endolysosomes during infections depending on the self-DNA characteristics and various inflammatory diseases. The fourth section discusses about AIM2 (an ALR), which also binds cytosolic self-DNA (with 80-300 base pairs or bp) that inhibits cGAS-STING-dependent type 1 IFN generation but induces inflammation and pyroptosis during different inflammatory conditions. Hence, this trinity of PRRs has evolved to recognize self-DNA as a potential DAMP and comes into action to guard the cellular galaxy. However, their dysregulation proves dangerous to the host and leads to several inflammatory conditions, including sterile-inflammatory conditions autoinflammatory and ADs.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor 9; absent in melanoma-2; absent in melanoma-2-like receptors; autoimmunity; cyclic GMP–AMP synthase; inflammation; stimulator of interferon genes.
Copyright © 2021 Kumar.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chakraborty M, Shashkova E, Cline-Smith A, Aurora R. Disruption of self-tolerance in autoimmune diseases and therapeutic modulation to restore immune balance. J Immunol (2018) 200(1 Supplement). 175.12-175.12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

