Developmental dysplasia of the hip screening programme in Chile
- PMID: 33643456
- PMCID: PMC7907761
- DOI: 10.1302/1863-2548.15.200240
Developmental dysplasia of the hip screening programme in Chile
Abstract
Purpose: Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) encompasses a wide pathological spectrum, from mild acetabular dysplasia to complete congenital hip dislocation at birth. Screening policies have been implemented in an effort to effectively identify and treat patients with DDH. Since 2009 there has been a national DDH programme in Chile. The current study evaluates the results of the programme in patients born between 2010 and 2015.
Methods: Records of patients hospitalized from 1st January 2010 to 31st December 2019 were retrieved from national databases. Those born from 1st January 2010 to 31st December 2015 who underwent a procedure for DDH under general anaesthesia during their first five years of life were selected. Sex, first surgical procedure and age at first surgical procedure were analyzed. The incidence of DDH that required major surgical treatment was calculated.
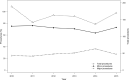
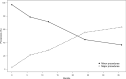
Results: A total of 961 children born from 1st January 2010 to 31st December 2015 underwent a procedure for DDH during their first five years of life. The number of major procedures was significantly lower than the number of minor procedures (269 vs 692). The incidence of major procedures was 0.18 per 1000 live births. Girls underwent a higher number of procedures than boys (831 vs 130), whereas 39.2% of the boys and 26.2% of the girls had major procedures. The mean age at the time of the first procedure was 15.35 months (sd 10.09; range 0.03 to 55.92 months).
Conclusion: The present study suggests that the Chilean National DDH Screening Program is an appropriate programme with substantial benefits with respect to public health.
Level of evidence: II.
Keywords: developmental dysplasia; hip; screening.
Copyright © 2020, The author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Weinstein SL, Mubarak SJ, Wenger DR. Developmental hip dysplasia and dislocation: part I. Instr Course Lect 2004;53:523-530. - PubMed
-
- Shaw BA, Segal LS. Section on orthopaedics. Evaluation and referral for developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants. Pediatrics 2016;138:e20163107. - PubMed
-
- Bialik V, Bialik GM, Blazer S, et al. . Developmental dysplasia of the hip: a new approach to incidence. Pediatrics 1999;103:93-99. - PubMed
-
- Grob J. Ultrasonografía: un método de pesquisa de la displasia y luxación congénita de la cadera. Rev Chilena Ortop y Traum 2000;41:7-16.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials