Nimodipine promotes neurite outgrowth and protects against neurotoxicity in PC12 cells
- PMID: 33643570
- PMCID: PMC7894639
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.48567.11152
Nimodipine promotes neurite outgrowth and protects against neurotoxicity in PC12 cells
Abstract
Objectives: Nimodipine is an L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC) antagonist. However, the actions of nimodipine except calcium blocking are poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate the effect of nimodipine on neurite outgrowth and neuroprotection in vitro.
Materials and methods: After PC12 cells were treated with different concentrations of nimodipine, neurite outgrowth was estimated using the ImageJ software. Neuroprotective effects of nimodipine against H2O2 and calcium ionophore-induced neurotoxicity were investigated using (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. In addition, the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and cyclic AMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) pathway was investigated for clarifying the action mechanism of nimodipine.
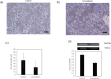
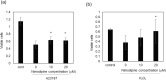
Results: Nimodipine treatment at doses of higher than 10 µM induced neurite outgrowth in the cells. Additionally, VDCC knockdown by siRNA significantly suppressed the nimodipine-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells, suggesting that the drug promotes neurite outgrowth by binding to VDCC. H2O2 and calcium ionophore induce oxidative and calcium stress in PC12 cells. Nimodipine exhibited neuroprotective effects against H2O2- and calcium ionophore-induced neurotoxicity by increasing the mRNA expression levels of neurotrophic factors, calcium-binding proteins, and antioxidants that are transcribed by CREB activation.
Conclusion: This is the first report that nimodipine induces neurite outgrowth and exerts its neuroprotective activity through the ERK/CREB signaling pathway in PC12 cells.
Keywords: Calcium channels; MAP kinase signaling – system; Neuronal outgrowth; Neuroprotection; Nimodipine.
Figures




References
-
- Findlay JM, Nisar J, Darsaut T. Cerebral vasospasm. A Review. Can J Neurol Sci. 2016;43:15–32. - PubMed
-
- Tomassoni D, Lanari A, Silvestrelli G, Traini E, Amenta F. Nimodipine and its use in cerebrovascular disease: Evidence from recent preclinical and controlled clinical studies. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2007;30:744–766. - PubMed
-
- Birks J, López-Arrieta J. Nimodipine for primary degenerative, mixed and vascular dementia. Cochrane Db Syst Rev. 2002:CD000147. - PubMed
-
- Scheller K, Scheller C. Nimodipine promotes regeneration of peripheral facial nerve function after traumatic injury following maxillofacial surgery: An off label pilot-study. J Cranio Maxill Surg. 2012;40:427–434. - PubMed
-
- Mattsson P, Janson AM, Aldskogius H, Svensson M. Nimodipine promotes regeneration and functional recovery after intracranial facial nerve crush. J Comp Neurol. 2001;437:106–117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
