Voluntary exercise improves spermatogenesis and testicular apoptosis in type 2 diabetic rats through alteration in oxidative stress and mir-34a/SIRT1/p53 pathway
- PMID: 33643571
- PMCID: PMC7894640
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.49498
Voluntary exercise improves spermatogenesis and testicular apoptosis in type 2 diabetic rats through alteration in oxidative stress and mir-34a/SIRT1/p53 pathway
Abstract
Objectives: This research was designed to demonstrate the impact of voluntary exercise on sperm parameters including sperm count, morphology, motility, viability, testicular apoptosis, oxidative stress, and the mir-34a/SIRT1/p53 pathway in type 2 diabetic rats.
Materials and methods: 32 Wistar male rats were separated into four groups: control (C), voluntary exercise (VE), diabetic (D), and diabetic rats that performed voluntary exercise (VED). To induce diabetes, animals were injected with streptozotocin (35 mg/kg) after receiving a high-fat diet. The testicular protein levels of SIRT1 and P53, miR-34a expression, MDA, GPx, SOD, catalase, and sperm parameters were evaluated.
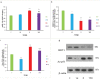
Results: Diabetes caused increased testicular MDA content, miR-34a expression, acetylated p53 protein expression, and the percent of immotile sperm (P<0.01 to P<0.001) as well as reduced testicular GPx, SOD and catalase activities, SIRT1 protein expression, and sperm parameters (P<0.05 to P<0.001). Voluntary exercise reduced testicular MDA content, miR-34a, and acetylated p53 protein expression compared with the D group (P<0.001), however, GPx, SOD, catalase activities, and sperm parameters in voluntarily exercised rats were elevated compared with diabetic rats (P<0.05 to P<0.001).
Conclusion: It seems that voluntary exercise has significant positive impacts that can be employed to reduce the complications of type 2 diabetes in the testis of male rats.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Oxidative stress; Sperm parameters; Type 2 diabetes; Voluntary exercise; miR-34a; p53.
Figures



References
-
- Shokri F, Shokoohi M, Niazkar HR, Abadi ARR, Kalarestaghi H, Ahin M. Investigation the spermatogenesis and testis structure in diabetic rats after treatment with Galega officinalis Extract. Crescent J Med Biol Sci. 2019;6:31–36.
-
- Bhattacharya SM, Ghosh M, Nandi N. Diabetes mellitus and abnormalities in semen analysis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2014;40:167–171. - PubMed
-
- Roessner C, Paasch U, Kratzsch J, Glander H-J, Grunewald S. Sperm apoptosis signalling in diabetic men. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012;25:292–299. - PubMed
-
- de Lamirande E, O’Flaherty C. Sperm activation: role of reactive oxygen species and kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1784:106–115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
