Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of a mitochondrial membrane-associated protein Cbs2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 33643713
- PMCID: PMC7896505
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10901
Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of a mitochondrial membrane-associated protein Cbs2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
Background: Mitochondria are unique organelles that are found in most eukaryotic cells. The main role of the mitochondria is to produce ATP. The nuclear genome encoded proteins Cbs1 and Cbs2 are located at the mitochondrial inner membrane and are reported to be essential for the translation of mitochondrial cytochrome b mRNA. Genetic studies show that Cbs2 protein recognizes the 5' untranslated leader sequence of mitochondrial cytochrome b mRNA. However, due to a lack of biochemical and structural information, this biological process remains unclear. To investigate the structural characteristics of how Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) Cbs2 tethers cytochrome b mRNA to the mitochondrial inner membrane, a preliminary X-ray crystallographic study was carried out and is reported here.
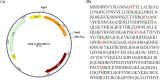
Methods: The target gene from S. cerevisiae was amplified by polymerase chain reaction. The PCR fragment was digested by the NdeI and XhoI restriction endonucleases and then inserted into expression vector p28. After sequencing, the plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli C43 competent cells. The selenomethionine derivative Cbs2 protein was overexpressed using M9 medium based on a methionine-biosynthesis inhibition method. The protein was first purified to Ni2+-nitrilotriacetate affinity chromatography and then further purified by Ion exchange chromatography and Gel-filtration chromatography. The purified Se-Cbs2 protein was concentrated to 10 mg/mL. The crystallization trials were performed using the sitting-drop vapor diffusion method at 16 °C. The complete diffraction data was processed and scaled with the HKL2000 package and programs in the CCP4 package, respectively.
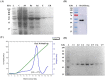
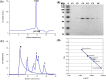
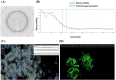
Results: Cbs2 from S. cerevisiae was cloned, prokaryotic expressed and purified. The analysis of the size exclusion chromatography showed that the Cbs2 protein peaked at a molecular weight of approximately 90 KDa. The crystal belonged to the space group C2, with unit-cell parameters of a = 255.11, b = 58.10, c = 76.37, and β = 95.35°. X-ray diffraction data was collected at a resolution of 2.7 Å. The Matthews coefficient and the solvent content were estimated to be 3.22 Å 3 Da-1 and 61.82%, respectively.
Conclusions: In the present study Cbs2 from S. cerevisiae was cloned, expressed, purified, and crystallized for structural studies. The molecular weight determination results indicated that the biological assembly of Cbs2 may be a dimer.The preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies indicated the presence of two Cbs2 molecules in the asymmetric unit. This study will provide an experimental basis for exploring how Cbs2 protein mediates cytochrome b synthesis.
Keywords: Cbs2; Crystallization; Cytochrome b; Expression and purification; Mitochondria.
©2021 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

