Design ensemble deep learning model for pneumonia disease classification
- PMID: 33643764
- PMCID: PMC7896551
- DOI: 10.1007/s13735-021-00204-7
Design ensemble deep learning model for pneumonia disease classification
Abstract
With the recent spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) has received more attention. The most important CAD application is to detect and classify pneumonia diseases using X-ray images, especially, in a critical period as pandemic of covid-19 that is kind of pneumonia. In this work, we aim to evaluate the performance of single and ensemble learning models for the pneumonia disease classification. The ensembles used are mainly based on fined-tuned versions of (InceptionResNet_V2, ResNet50 and MobileNet_V2). We collected a new dataset containing 6087 chest X-ray images in which we conduct comprehensive experiments. As a result, for a single model, we found out that InceptionResNet_V2 gives 93.52% of F1 score. In addition, ensemble of 3 models (ResNet50 with MobileNet_V2 with InceptionResNet_V2) shows more accurate than other ensembles constructed (94.84% of F1 score).
Keywords: Computer-aided diagnosis; Covid-19; Deep learning; Ensemble deep learning; Pneumonia disease; Pneumonia multiclass classification; X-ray images.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag London Ltd. part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestWe declare that we have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Author has no received research grants from any company.
Figures
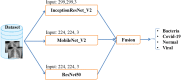
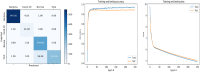
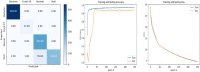
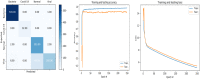
References
-
- Elasnaoui K, Chawki Y, Radeva P, Idri A (2020) Automated methods for detection and classification pneumonia based on X-ray images using deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.14363
-
- Zerouaoui H, Idri A, El Asnaoui K (2020) Machine learning and image processing for breast cancer: a systematic map. In: World conference on information systems and technologies. Springer, Cham, pp 44–53
-
- Ouhda M, El Asnaoui K, Ouanan M, Aksasse B (2017) Content-based image retrieval using convolutional neural networks. In: First international conference on real time intelligent systems. Springer, Cham, pp 463–476
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
