Global Research Trends on Prostate Diseases and Erectile Dysfunction: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study
- PMID: 33643922
- PMCID: PMC7908828
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.627891
Global Research Trends on Prostate Diseases and Erectile Dysfunction: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study
Abstract
Objectives: To identify the cooperation of authors, countries, institutions and explore the hot topics' prospects regarding research of prostate diseases and erectile dysfunction (ED).
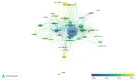
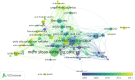
Methods: Publications on research of prostate diseases and ED were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC). Bibliometric analyses were performed using VOSviewer and CiteSpace software. Network maps were generated to evaluate the collaborations between different authors, countries, institutions, and keywords.
Results: A total of 2,599 articles related to study of prostate diseases and ED were identified. We observed gradually increasing in the number of publications from 1998 to 2016, and the trend was to be relatively stable in the past 3 years. Journal of Sexual Medicine (243 papers) owned the highest number of publications and Journal of Urology was the most co-cited journal. Mulhall John P (52 papers) was the top most productive authors and Mcvary Kebin T with the largest numbers of citations (1,589 co-citations) during the past decades. There were active collaborations among the top authors. The USA was the leading contributor in this field with 1,078 papers. Active cooperation between countries and between institutions was observed. The main hot topics included matters related to erectile dysfunction, prostate cancer, quality-of-life, radical prostatectomy, sexual function, and BPH.
Conclusion: Bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the development of scientific literature, allowing relevant authors and research teams to recognize the current research status in this field and at the same time provide a reference for formulating future research directions.
Keywords: benign prostatic hyperplasia; bibliometric analysis; erectile dysfunction; prostate cancer; radical prostatectomy.
Copyright © 2021 Ma, Su and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Coughlin GD, Yaxley JW, Chambers SK, Occhipinti S, Samaratunga H, Zajdlewicz L, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy versus open radical retropubic prostatectomy: 24-month outcomes from a randomised controlled study. Lancet Oncol (2018) 19(8):1051–60. 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30357-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vuichoud C, Loughlin KR. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: epidemiology, economics and evaluation. Can J Urol (2015) 22 Suppl 1:1–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

