Mechanobiological Principles Influence the Immune Response in Regeneration: Implications for Bone Healing
- PMID: 33644014
- PMCID: PMC7907627
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.614508
Mechanobiological Principles Influence the Immune Response in Regeneration: Implications for Bone Healing
Abstract
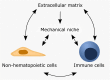
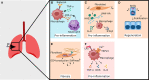
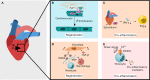
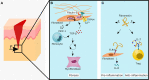
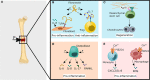
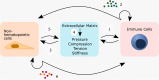
A misdirected or imbalanced local immune composition is often one of the reasons for unsuccessful regeneration resulting in scarring or fibrosis. Successful healing requires a balanced initiation and a timely down-regulation of the inflammation for the re-establishment of a biologically and mechanically homeostasis. While biomaterial-based approaches to control local immune responses are emerging as potential new treatment options, the extent to which biophysical material properties themselves play a role in modulating a local immune niche response has so far been considered only occasionally. The communication loop between extracellular matrix, non-hematopoietic cells, and immune cells seems to be specifically sensitive to mechanical cues and appears to play a role in the initiation and promotion of a local inflammatory setting. In this review, we focus on the crosstalk between ECM and its mechanical triggers and how they impact immune cells and non-hematopoietic cells and their crosstalk during tissue regeneration. We realized that especially mechanosensitive receptors such as TRPV4 and PIEZO1 and the mechanosensitive transcription factor YAP/TAZ are essential to regeneration in various organ settings. This indicates novel opportunities for therapeutic approaches to improve tissue regeneration, based on the immune-mechanical principles found in bone but also lung, heart, and skin.
Keywords: PIEZO1; TRPV4; YAP/TAZ; immune-mechanics; inflammation; mechano-transduction; mechanobiology; regeneration.
Copyright © 2021 Knecht, Bucher, Van Linthout, Tschöpe, Schmidt-Bleek and Duda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ara T., Itoi M., Kawabata K., Egawa T., Tokoyoda K., Sugiyama T., et al. (2003). A Role of CXC chemokine ligand 12/stromal cell-derived factor-1/Pre-B cell growth stimulating factor and its receptor CXCR4 in fetal and adult T cell development in vivo. J. Immunol. 170, 4649–4655. 10.4049/jimmunol.170.9.4649 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

