High Prevalence of Ultrasound Verified Enthesitis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease With or Without Spondylarthritis
- PMID: 33644102
- PMCID: PMC7906964
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.637459
High Prevalence of Ultrasound Verified Enthesitis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease With or Without Spondylarthritis
Abstract
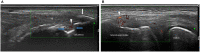
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is closely associated with spondylarthritis (SpA) and enthesitis, as an important feature of SpA, is a common extraintestinal manifestation of IBD. Enthesitis may be clinically silent in a high proportion of patients with IBD without clinical signs or a diagnosis of SpA. Objectives: The aim of this study was to compare the prevalence of ultrasound (US) verified enthesitis in IBD patients with and without SpA, with patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and healthy subjects (HC) serving as controls. Methods: IBD patients with or without SpA, patients with IBS and HC were prospectively recruited and clinically assessed. Ultrasound examination was performed at 14 entheses. The ultrasound abnormalities were scored according to the Madrid Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesitis Index (MASEI). Results: We included 33 IBD patients without SpA, 14 IBD patients with SpA, 26 IBS patients and 18 HC. Higher MASEI scores were found in patients with IBD without SpA [median 21.0 range (8.0-53.0)] and IBD associated SpA [33.0 (8-50)] than in IBS patients [10.5 (0-42.0)-p < 0.001 for both comparison] and HC [12.0 (2.0-38.0)-p < 0.01]. PD, enthesophytes and erosions were more common in patients with IBD with or without SpA as compared to IBS patients and HC. IBD patients with SpA compared to IBD without SpA demonstrated significant higher prevalence of erosion and structural irregularity and consequently significant higher MASEI (p < 0.05 for all comparison). Conclusions: Ultrasound verified enthesitis is more common in patients with IBD with or without SpA as compared to patients with IBS or HC.
Keywords: enthesitis; inflammatory bowel diseases; power Doppler ultrasonography; spondyloarthropathies; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2021 Husic, Lackner, Kump, Högenauer, Graninger and Dejaco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enthesitis in IBD Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 3;13(15):4540. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154540. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and ultrasonographic enthesopathy in inflammatory rheumatic diseases : Is MASEI or only calcaneal enthesitis sufficient?Z Rheumatol. 2018 Oct;77(8):719-726. doi: 10.1007/s00393-017-0405-2. Z Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29116386 English.
-
Power Doppler signal at the enthesis and bone erosions are the most discriminative OMERACT ultrasound lesions for SpA: results from the DEUS (Defining Enthesitis on Ultrasound in Spondyloarthritis) multicentre study.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Jun 12;83(7):847-857. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-225443. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38443140
-
Case-control Study on Dactylitis, Enthesitis, and Anterior Uveitis in Spondyloarthritis Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Role of Coexistent Psoriasis.J Rheumatol. 2017 Sep;44(9):1341-1346. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.161518. Epub 2017 Apr 15. J Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28412702
-
Frequency of irritable bowel syndrome in spondyloarthritis: a multicentric cross-sectional study and meta-analysis.RMD Open. 2024 Jan 12;10(1):e003836. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003836. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 38216286 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Practical Tips for Diagnosis and Management of Concomitant Inflammatory Spondyloarthritis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025 Jul 14;27(1):52. doi: 10.1007/s11894-025-00990-8. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40658153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound to Identify Subclinical Joint and Periarticular Involvement in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Literature Review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 16;9:919521. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.919521. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35652081 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatic Manifestations in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single Tertiary Centre, Interdisciplinary Study.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2025 May 23;36(2):215-219. doi: 10.31138/mjr.291123.ept. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40757119 Free PMC article.
-
Enthesitis in IBD Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 3;13(15):4540. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154540. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mielants H, Veys EM, Cuvelier C, De Vos M, Goemaere S, De Clercq L, et al. . The evolution of spondyloarthropathies in relation to gut histology. III. Relation between gut and joint. J Rheumatol. (1995) 22:2279–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials