SIMR foci are found in the progenitor germ cells of C. elegans embryos
- PMID: 33644707
- PMCID: PMC7900827
- DOI: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000374
SIMR foci are found in the progenitor germ cells of C. elegans embryos
Abstract
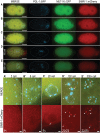
RNA interference is a widely conserved mechanism of gene regulation and silencing across eukaryotes. In C. elegans, RNA silencing is coordinated through perinuclear nuage containing at least four granules: P granules, Z granules, Mutator foci, and SIMR foci. Embryonic localization of these granules is known for all except SIMR foci. Here we establish that SIMR foci first appear at the nuclear periphery in the P4 germline blastomere and become numerous and bright in the Z2 and Z3 progenitor germ cells. This timing coincides with the appearance or de-mixing of other germline granules, providing further evidence for coordinated germ granule reorganization.
Copyright: © 2021 by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Manage KI, Rogers AK, Wallis DC, Uebel CJ, Anderson DC, Nguyen DAH, Arca K, Brown KC, Cordeiro Rodrigues RJ, de Albuquerque BF, Ketting RF, Montgomery TA, Phillips CM. A tudor domain protein, SIMR-1, promotes siRNA production at piRNA-targeted mRNAs in C. elegans. Elife. 2020 Apr 27;9 doi: 10.7554/eLife.56731. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
