Stereotactic body radiotherapy for synchronous early stage non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 33645424
- PMCID: PMC8996167
- DOI: 10.1080/0284186X.2021.1892182
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for synchronous early stage non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Introduction: In patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who present with multiple pulmonary nodules, it is often difficult to distinguish metastatic disease from synchronous primary lung cancers (SPLC). We sought to evaluate clinical outcomes after stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) alone to synchronous primary lesions.
Material and methods: Patients with synchronous AJCC 8th Edition Stage IA-IIA NSCLC and treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) to all lesions between 2009-2018 were reviewed. SPLC was defined as patients having received two courses of SBRT within 180 days for treatment of separate early stage tumors. In total, 36 patients with 73 lesions were included. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), cumulative incidence of local failure (LF), and regional/distant failure (R/DF) were estimated and compared with a control cohort of solitary early stage NSCLC patients.
Results: Median PFS was 38.8 months (95% CI 14.3-not reached [NR]); 3-year PFS rates were 50.6% (35.6-72.1). Median OS was 45.9 months (95% CI: 35.9-NR); 3-year OS was 63.0% (47.4-83.8). Three-year cumulative incidence of LF and R/DF was 6.6% (3.7-13.9) and 35.7% (19.3-52.1), respectively. Patients with SPLC were compared to a control group (n = 272) of patients treated for a solitary early stage NSCLC. There was no statistically significant difference in PFS (p = .91) or OS (p = .43). Evaluation of the patterns of failure showed a trend for worse cumulative incidence of R/DF in SPLC patients as compared to solitary early stage NSCLC (p = .06).
Conclusion: SBRT alone to multiple lung tumors with SPLC results in comparable PFS, OS, and LF rates to a cohort of patients treated for solitary early stage NSCLC. Those with SPLC had non-significantly higher R/DF. Patients with SPLC should be followed closely for failure and possible salvage therapy.
Keywords: NSCLC; SBRT; lung cancer; metachronous primary lung cancer; radiation therapy; synchronous primary lung cancer.
Figures

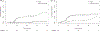
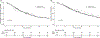
Similar articles
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) improves local control and overall survival compared to conventionally fractionated radiation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Acta Oncol. 2018 Nov;57(11):1567-1573. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2018.1481292. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Acta Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29873277 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrence Patterns and Second Primary Lung Cancers After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Surveillance.Clin Lung Cancer. 2016 May;17(3):177-183.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Clin Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26602271 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of accelerated hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiotherapy for Stage 1 and node negative Stage 2 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2014 Jul;85(1):59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24813936 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for early-stage lung cancer in the elderly.Semin Oncol. 2018 Aug;45(4):210-219. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jul 1. Semin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30286944 Review.
-
Local control correlates with overall survival in radiotherapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review.Radiother Oncol. 2023 Jun;183:109664. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2023.109664. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Radiother Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37024056
Cited by
-
Multiple primary lung cancer: Updates of clinical management and genomic features.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 22;13:1034752. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1034752. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36910635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT): Challenging Scenarios and New Frontiers.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 9;14(14):4871. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144871. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose-effect relationship of stereotactic body radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients.Radiat Oncol. 2022 Dec 23;17(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02183-3. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36564845 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Multiple Primary Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 4;14(1):242. doi: 10.3390/cancers14010242. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35008406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis and management of multiple primary lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 1;14:1392969. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1392969. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39411141 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Videtic GMM, Donington J, Giuliani M, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: executive summary of an ASTRO evidence-based guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017;7(5):295–301. - PubMed
-
- Videtic GMM, Hu C, Singh AK, et al. A randomized phase 2 study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage i peripheral non-small cell lung cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93(4):757–764. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
