Nanosac, a Noncationic and Soft Polyphenol Nanocapsule, Enables Systemic Delivery of siRNA to Solid Tumors
- PMID: 33645963
- PMCID: PMC8023695
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c08694
Nanosac, a Noncationic and Soft Polyphenol Nanocapsule, Enables Systemic Delivery of siRNA to Solid Tumors
Abstract
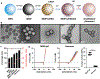
For systemic delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to solid tumors, the carrier must circulate avoiding premature degradation, extravasate and penetrate tumors, enter target cells, traffic to the intracellular destination, and release siRNA for gene silencing. However, existing siRNA carriers, which typically exhibit positive charges, fall short of these requirements by a large margin; thus, systemic delivery of siRNA to tumors remains a significant challenge. To overcome the limitations of existing approaches, we have developed a carrier of siRNA, called "Nanosac", a noncationic soft polyphenol nanocapsule. A siRNA-loaded Nanosac is produced by sequential coating of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) with siRNA and polydopamine, followed by removal of the sacrificial MSN core. The Nanosac recruits serum albumin, co-opts caveolae-mediated endocytosis to enter tumor cells, and efficiently silences target genes. The softness of Nanosac improves extravasation and penetration into tumors compared to its hard counterpart. As a carrier of siRNA targeting PD-L1, Nanosac induces a significant attenuation of CT26 tumor growth by immune checkpoint blockade. These results support the utility of Nanosac in the systemic delivery of siRNA for solid tumor therapy.
Keywords: immune checkpoint blockade; noncationic; polyphenol nanocapsules; siRNA; soft; solid tumors; systemic delivery.
Figures




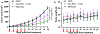
References
-
- Hannon GJ, RNA Interference. Nature 2002, 418 (6894), 244–251. - PubMed
-
- Devi GR, siRNA-Based Approaches in Cancer Therapy. Cancer Gene Therapy 2006, 13 (9), 819–829. - PubMed
-
- Choung S; Kim YJ; Kim S; Park H-O; Choi Y-C, Chemical Modification of siRNAs to Improve Serum Stability without Loss of Efficacy. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2006, 342 (3), 919–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

