Diclofenac-induced cytotoxicity in cultured carp leukocytes
- PMID: 33646004
- PMCID: PMC8603699
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.934609
Diclofenac-induced cytotoxicity in cultured carp leukocytes
Abstract
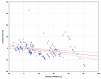
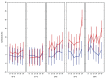
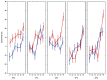
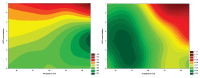
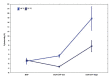
Diclofenac is a drug commonly used in human and veterinary medicine for the treatment of diseases associated with inflammation and pain. Medicinal products enter waste and surface waters on an everyday basis and contaminate the aquatic environment. Fish are therefore permanently exposed to these chemicals dissolved in their aquatic environment. To simulate variable environmental conditions, the aim of our study was to examine adverse effects of diclofenac under different temperatures of cell incubation (18, 21, 24, 27 and 30 °C). Cyto-toxic and -static effects of diclofenac in concentrations of 0.001 mcg/ml, 0.01 microg/ml, 0.1 mcg/ml, 1 mcg/ml, 10 mcg/ml and 100 mcg/ml for the carp (Cyprinuscarpio) cultured leukocytes were quantified using detection of lactate dehydrogenase released from damaged cells. Overall DCF cytotoxicity was relatively low and its impact was pronounced at higher temperature and DCF concentration. Cells growth inhibition is changing more rapidly but it is high mainly at the highest concentration from low temperature. DNA fragmentation was not detected in tested leukocyte cell line. CYP450 increased diclofenac cytotoxicity only at the highest concentration but at incubation temperatures 18 and 27 °C. Leukocyte viability is essential for immune functions and any change can lead to reduction of resistance against pathogens, mainly in cold year seasons, when the immune system is naturally suppressed.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- ABDELSALAM EEE, BANDOUCHOVA H, HEGER T, KANOVA M, KOBELKOVA K, NĚMCOVÁ M, PIAČEK V, SEDLACKOVA J, SEIDLOVA V, VITULA F, PIKULA J. Polychlorinated biphenyl toxicity in the thyroid gland of wild ungulates: an in vitro model. Acta Veterinaria Brno. 2020;89:151–162. doi: 10.2754/avb202089020151. - DOI
-
- ARNOLD KE, BOXALL ABA, BROWN AR, CUTHBURT RJ, GAW S, HUTCHINSON TH, JOBLING S, MADDEN JC, METCALFE CD, NAIDOO V, SHORE RF, SMITS JE, TAGGART MA, THOMPSON HM. Assessing the exposure risk and impacts of pharmaceuticals in the environment on individuals and ecosystems. Biol Lett. 2013;9:1–4. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2013.0492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
