Highly functional virus-specific cellular immune response in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 33646265
- PMCID: PMC7927662
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20202617
Highly functional virus-specific cellular immune response in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
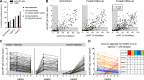
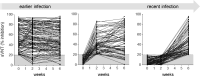
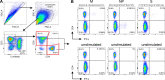
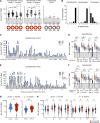
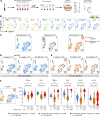
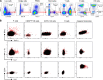
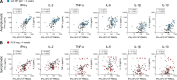
The efficacy of virus-specific T cells in clearing pathogens involves a fine balance between antiviral and inflammatory features. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in individuals who clear SARS-CoV-2 without symptoms could reveal nonpathological yet protective characteristics. We longitudinally studied SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in a cohort of asymptomatic (n = 85) and symptomatic (n = 75) COVID-19 patients after seroconversion. We quantified T cells reactive to structural proteins (M, NP, and Spike) using ELISpot and cytokine secretion in whole blood. Frequencies of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells were similar between asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals, but the former showed an increased IFN-γ and IL-2 production. This was associated with a proportional secretion of IL-10 and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β) only in asymptomatic infection, while a disproportionate secretion of inflammatory cytokines was triggered by SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell activation in symptomatic individuals. Thus, asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals are not characterized by weak antiviral immunity; on the contrary, they mount a highly functional virus-specific cellular immune response.
© 2021 Le Bert et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: N. Le Bert and A.T. Tan reported a patent for a method to monitor SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in biological samples pending. W.N. Chia reported a patent for a sublicense agreement with GenScript for the surrogate virus neutralization test pending (Duke-NUS). P. Tambyah reported grants from Arcturus, Roche, Shionogi, Sanofi-Pasteur, and Aj Biologics outside the submitted work. L. Wang reported a patent application on sVNT pending. A. Bertoletti reported personal fees from Oxford Immunotech and Qiagen outside the submitted work; in addition, A. Bertoletti had a patent for the use of peptide pools in whole blood for detection of SARS-CoV-2 T cells pending. C.C. Tam reported grants from Roche and personal fees from Verivax outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures




References
-
- Cervia, C., Nilsson J., Zurbuchen Y., Valaperti A., Schreiner J., Wolfensberger A., Raeber M.E., Adamo S., Emmenegger M., Hasler S., et al. 2020. Systemic and mucosal antibody secretion specific to SARS-CoV-2 during mild versus severe COVID-19. bioRxiv. 10.1101/2020.05.21.108308 (Preprint posted May 23, 2020) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Biasi, S., Meschiari M., Gibellini L., Bellinazzi C., Borella R., Fidanza L., Gozzi L., Iannone A., Lo Tartaro D., Mattioli M., et al. 2020. Marked T cell activation, senescence, exhaustion and skewing towards TH17 in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Nat. Commun. 11:3434. 10.1038/s41467-020-17292-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

