Haploidentical age-adapted myeloablative transplant and regulatory and effector T cells for acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 33646302
- PMCID: PMC7948281
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003739
Haploidentical age-adapted myeloablative transplant and regulatory and effector T cells for acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
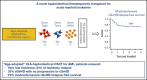
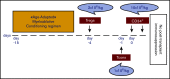
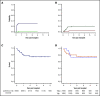
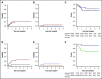
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the most effective treatment in eradicating high-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Here, we present data from a novel HLA-haploidentical HSCT protocol that addressed the 2 remaining major unmet medical needs: leukemia relapse and chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD). Fifty AML patients were enrolled in the study. The conditioning regimen included total body irradiation for patients up to age 50 years and total marrow/lymphoid irradiation for patients age 51 to 65 years. Irradiation was followed by thiotepa, fludarabine, and cyclophosphamide. Patients received an infusion of 2 × 106/kg donor regulatory T cells on day -4 followed by 1 × 106/kg donor conventional T cells on day -1 and a mean of 10.7 × 106 ± 3.4 × 106/kgpurified CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells on day 0. No pharmacological GVHD prophylaxis was administered posttransplantation. Patients achieved full donor-type engraftment. Fifteen patients developed grade ≥2 acute GVHD (aGVHD). Twelve of the 15 patients with aGVHD were alive and no longer receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Moderate/severe cGVHD occurred in only 1 patient. Nonrelapse mortality occurred in 10 patients. Only 2 patients relapsed. Consequently, at a median follow-up of 29 months, the probability of moderate/severe cGVHD/relapse-free survival was 75% (95% confidence interval, 71%-78%). A novel HLA-haploidentical HSCT strategy that combines an age-adapted myeloablative conditioning regimen with regulatory and conventional T-cell adoptive immunotherapy resulted in an unprecedented cGVHD/relapse-free survival rate in 50 AML patients with a median age of 53 years. This trial was registered with the Umbria Region Institutional Review Board Public Registry as identification code 02/14 and public registry #2384/14 and at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT03977103.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cornelissen JJ, Gratwohl A, Schlenk RF, et al. The European LeukemiaNet AML Working Party consensus statement on allogeneic HSCT for patients with AML in remission: an integrated-risk adapted approach. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9(10):579-590. - PubMed
-
- Cornelissen JJ, Blaise D. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with AML in first complete remission. Blood. 2016;127(1):62-70. - PubMed
-
- Bashey A, Zhang X, Sizemore CA, et al. T-cell-replete HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic transplantation for hematologic malignancies using post-transplantation cyclophosphamide results in outcomes equivalent to those of contemporaneous HLA-matched related and unrelated donor transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(10):1310-1316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

