Prostate cancer follow-up costs in Germany from 2000 to 2015
- PMID: 33646503
- PMCID: PMC8881276
- DOI: 10.1007/s11764-021-01006-w
Prostate cancer follow-up costs in Germany from 2000 to 2015
Abstract
Purpose: The main objective of this study is to estimate and evaluate 10-year follow-up costs after prostate cancer treatment with curative (surgery, radiotherapy) and non-curative intent (hormone, androgen deprivation) per patient in Germany in 2000, 2008, and 2015.
Methods: Prostate cancer follow-up recommendations were extracted from the European Association of Urology guidelines from 2000 to 2015. Per patient costs were calculated with a detailed micro-costing approach considering direct and indirect medical expenses. Input parameters were derived from expert interviews, literature research, and official scales of tariffs. Costs for insurers, providers, and payers were included to estimate societal costs.
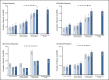
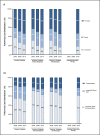
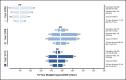
Results: Mean 10-year follow-up costs per patient after treatment with curative intent amounted to EUR 4415 in 2000, EUR 4224 in 2008 (p < 0.001), and EUR 5159 in 2015 (p < 0.001). Costs after hormone therapy with metastasis cumulated to EUR 10,846 in 2000, EUR 9818 in 2008 (p < 0.001), and EUR 11,978 in 2015 (p < 0.001). While insurers covered 37% of costs in 2000 (EUR 1664), only 23% of costs were reimbursed in 2015 (EUR 1195; p < 0.001). Cost sources mainly included consultations (55%), transportation (18%), and imaging (27%).
Conclusion: Early detection and advances in prostate cancer treatment increased 10-year survival rates beyond 80% in Germany, ultimately expanding the number of survivors requiring follow-up. Statutory insurers reacted by decreasing the reimbursement rates to reduce per patient cost by up to 46%. Consequently, the economic burden was mainly shifted to payers and providers.
Implications for cancer survivors: Equitable and effective follow-up schedules covered by insurance funds are necessary to care for prostate cancer patients.
Keywords: Budget impact; Cost; Follow-up; Health insurance; Prostate cancer.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Böhm K, Mardorf S, Nöthen M, et al. Beiträge zur Gesundheitsberichterstattung des Bundes - Gesundheit und Krankheit im Alter. Berlin: Robert Koch-Institut; 2009.
-
- Robert Koch Institute . Cancer in Germany 2015/2016. 12. Berlin: Robert Koch Institute; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

