Growth Failure Prevalence in Neonates with Gastroschisis : A Statewide Cohort Study
- PMID: 33647253
- PMCID: PMC8154735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.02.013
Growth Failure Prevalence in Neonates with Gastroschisis : A Statewide Cohort Study
Abstract
Objectives: To perform a multicenter study to assess growth failure in hospitalized infants with gastroschisis.
Study design: This study included neonates with gastroschisis within sites in the University of California Fetal Consortium. The study's primary outcome was growth failure at hospital discharge, defined as a weight or length z score decrease >0.8 from birth. Regression analysis was performed to assess changes in z scores over time.
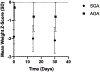
Results: Among 125 infants with gastroschisis, the median gestational age was 37 weeks (IQR 35-37). Length of stay was 32 days (23-60); 55% developed weight or length growth failure at discharge (28% had weight growth failure, 42% had length growth failure, and 15% had both weight and length growth failure). Weight and length z scores at 14 days, 30 days, and discharge were less than birth (P < .01 for all). Weight and length z scores declined from birth to 30 days (-0.10 and -0.11 z score units/week, respectively, P < .001). Length growth failure at discharge was associated with weight and length z score changes over time (P < .05 for both). Lower gestational age was associated with weight growth failure (OR 0.70 for each gestational age week, 95% CI 0.55-0.89, P = .004).
Conclusions: Growth failure, in particular linear growth failure, is common in infants with gastroschisis. These data suggest the need to improve nutritional management in these infants.
Keywords: gastrointestinal anomaly; growth velocity; infants; prematurity; z score.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
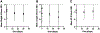
References
-
- Corkins MR, Guenter P, DiMaria-Ghalili RA, Jensen GL, Malone A, Miller S, et al. Malnutrition diagnoses in hospitalized patients: United States, 2010. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014;38: 186–195. - PubMed
-
- Irving SY, Daly B, Verger J, Typpo K, Brown A, Hanlon A, et al. The Association of Nutrition Status Expressed as Body Mass Index z Score With Outcomes in Children With Severe Sepsis: A Secondary Analysis From the Sepsis Prevalence, Outcomes, and Therapies (SPROUT) Study. Crit Care Med. 2018;46: e1029–e1039. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ehrenkranz RA, Dusick AM, Vohr BR, Wright LL, Wrage LA, and Poole WK. Growth in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Influences Neurodevelopmental and Growth Outcomes of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics April 2006; 117: 1253–1261. - PubMed
-
- Wiedmeier JE, Joss-Moore LA, Lane RH, and Neu J. Early postnatal nutrition and programming of the preterm neonate. Nutrition Reviews February 2011; 69: 76–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

