Combination therapy with tocilizumab and corticosteroids for aged patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A single-center retrospective study
- PMID: 33647515
- PMCID: PMC7908857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.099
Combination therapy with tocilizumab and corticosteroids for aged patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A single-center retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The role of combination immunomodulatory therapy with systemic corticosteroids and tocilizumab (TCZ) for aged patients with COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome remains unclear.
Methods: A retrospective single-center study was conducted on consecutive patients aged ≥65 years who developed severe COVID-19 between 03 March and 01 May 2020 and were treated with corticosteroids at various doses (methylprednisolone 0.5mg/kg/12h to 250mg/24h), either alone (CS group) or associated with intravenous tocilizumab (400-600mg, one to three doses) (CS-TCZ group). The primary outcome was all-cause mortality by day +14, whereas secondary outcomes included mortality by day +28 and clinical improvement (discharge and/or a ≥2 point decrease on a 6-point ordinal scale) by day +14. Propensity score (PS)-based adjustment and inverse probability of treatment weights (IPTW) were applied.
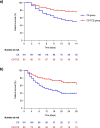
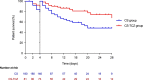
Results: Totals of 181 and 80 patients were included in the CS and CS-TCZ groups, respectively. All-cause 14-day mortality was lower in the CS-TCZ group, both in the PS-adjusted (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.34; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.17-0.68; P=0.002) and IPTW-weighted models (odds ratio [OR]: 0.38; 95% CI: 0.21-0.68; P=0.001). This protective effect was also observed for 28-day mortality (PS-adjusted HR: 0.38; 95% CI: 0.21-0.72; P=0.003). Clinical improvement by day +14 was higher in the CS-TCZ group with IPTW analysis only (OR: 2.26; 95% CI: 1.49-3.41; P<0.001). The occurrence of secondary infection was similar between both groups.
Conclusions: The combination of corticosteroids and TCZ was associated with better outcomes among patients aged ≥65 years with severe COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Corticosteroids; Immunomodulation; Mortality; Outcome; SARS-CoV-2; Therapy; Tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneficial and harmful outcomes of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharmacotherapy. 2021 Nov;41(11):884-906. doi: 10.1002/phar.2627. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Pharmacotherapy. 2021. PMID: 34558742 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effect of corticosteroids in preventing mortality in patients receiving tocilizumab to treat severe COVID-19 illness.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Dec;101:290-297. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.1486. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33035673 Free PMC article.
-
Tocilizumab for the treatment of adult patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A single-center cohort study.J Med Virol. 2021 Feb;93(2):831-842. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26308. Epub 2020 Jul 27. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32672860 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Tocilizumab vs Usual Care in Adults Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Moderate or Severe Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Jan 1;181(1):32-40. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820. JAMA Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33080017 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: A single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy.Autoimmun Rev. 2020 Jul;19(7):102568. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568. Epub 2020 May 3. Autoimmun Rev. 2020. PMID: 32376398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tocilizumab and Systemic Corticosteroids in the Management of Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Sep;110:320-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.07.021. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34273515 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial and harmful outcomes of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharmacotherapy. 2021 Nov;41(11):884-906. doi: 10.1002/phar.2627. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Pharmacotherapy. 2021. PMID: 34558742 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy of tocilizumab and steroid for COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2022 Apr;94(4):1350-1356. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27489. Epub 2021 Dec 7. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34850411 Free PMC article.
-
An updated overview of recent advances, challenges, and clinical considerations of IL-6 signaling blockade in severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Apr;105:108536. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108536. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35074571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Date of Admission during COVID-19 Pandemic Impacted Patient Outcomes in Addition to the Higher Efficacy of Tocilizumab Plus High-Dose Corticosteroid Therapy Compared to Tocilizumab Alone.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 30;11(1):198. doi: 10.3390/jcm11010198. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 35011938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canziani L.M., Trovati S., Brunetta E., Testa A., De Santis M., Bombardieri E. Interleukin-6 receptor blocking with intravenous tocilizumab in COVID-19 severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective case-control survival analysis of 128 patients. J Autoimmun. 2020;114 doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102511. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

