Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease
- PMID: 33649162
- PMCID: PMC7919414
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.346312.120
Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease
Abstract
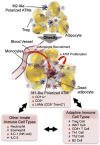
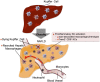
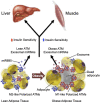
Obesity is the most common cause of insulin resistance, and the current obesity epidemic is driving a parallel rise in the incidence of T2DM. It is now widely recognized that chronic, subacute tissue inflammation is a major etiologic component of the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Here, we summarize recent advances in our understanding of immunometabolism. We discuss the characteristics of chronic inflammation in the major metabolic tissues and how obesity triggers these events, including a focus on the role of adipose tissue hypoxia and macrophage-derived exosomes. Last, we also review current and potential new therapeutic strategies based on immunomodulation.
Keywords: glucose intolerance; immunometabolism; inflammation; insulin resistance; macrophage; metaflammation; β-cell dysfunction.
© 2021 Lee and Olefsky; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Amar J, Chabo C, Waget A, Klopp P, Vachoux C, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Smirnova N, Bergá M, Sulpice T, Lahtinen S, et al. 2011. Intestinal mucosal adherence and translocation of commensal bacteria at the early onset of type 2 diabetes: molecular mechanisms and probiotic treatment. EMBO Mol Med 3: 559–572. 10.1002/emmm.201100159 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
