Iron overload in aging Bmp6‑/‑ mice induces exocrine pancreatic injury and fibrosis due to acinar cell loss
- PMID: 33649802
- PMCID: PMC7910010
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4893
Iron overload in aging Bmp6‑/‑ mice induces exocrine pancreatic injury and fibrosis due to acinar cell loss
Abstract
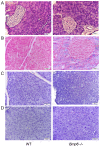
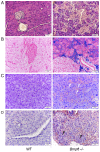
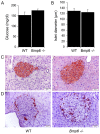
The relationship between hemochromatosis and diabetes has been well established, as excessive iron deposition has been reported to result in impaired function of the endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Therefore, the objective of the present study was to analyze the effects of iron accumulation on the pancreata and glucose homeostasis in a bone morphogenetic protein 6‑knockout (Bmp6‑/‑) mouse model of hemochromatosis. The sera and pancreatic tissues of wild‑type (WT) and Bmp6‑/‑ mice (age, 3 and 10 months) were subjected to biochemical and histological analyses. In addition, 18F‑fluorodeoxyglucose biodistribution was evaluated in the liver, muscle, heart, kidney and adipose tissue of both animal groups. The results demonstrated that 3‑month‑old Bmp6‑/‑ mice exhibited iron accumulation preferentially in the exocrine pancreas, with no signs of pancreatic injury or fibrosis. No changes were observed in the glucose metabolism, as pancreatic islet diameter, insulin and glucagon secretion, blood glucose levels and glucose uptake in the liver, muscle and adipose tissue remained comparable with those in the WT mice. Aging Bmp6‑/‑ mice presented with progressive iron deposits in the exocrine pancreas, leading to pancreatic degeneration and injury that was characterized by acinar atrophy, fibrosis and the infiltration of inflammatory cells. However, the aging mice exhibited unaltered blood glucose levels and islet structure, normal insulin secretion and moderately increased α‑cell mass compared with those in the age‑matched WT mice. Additionally, iron overload and pancreatic damage were not observed in the aging WT mice. These results supported a pathogenic role of iron overload in aging Bmp6‑/‑ mice leading to iron‑induced exocrine pancreatic deficiency, whereas the endocrine pancreas retained normal function.
Keywords: bone morphogenetic protein 6; glucose homeostasis; pancreas; iron metabolism; diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lack of the bone morphogenetic protein BMP6 induces massive iron overload.Nat Genet. 2009 Apr;41(4):478-81. doi: 10.1038/ng.320. Epub 2009 Mar 1. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19252488
-
Hepcidin knockout mice spontaneously develop chronic pancreatitis owing to cytoplasmic iron overload in acinar cells.J Pathol. 2017 Jan;241(1):104-114. doi: 10.1002/path.4822. Epub 2016 Dec 1. J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27741349
-
Evaluation of a bone morphogenetic protein 6 variant as a cause of iron loading.Hum Genomics. 2018 Apr 25;12(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40246-018-0155-5. Hum Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29695288 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose homeostasis dependency on acini-islet-acinar (AIA) axis communication: a new possible pathophysiological hypothesis regarding diabetes mellitus.Nutr Diabetes. 2018 Oct 8;8(1):55. doi: 10.1038/s41387-018-0062-9. Nutr Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 30293998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMP-6 and mesenchymal stem cell differentiation.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009 Oct-Dec;20(5-6):441-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.10.020. Epub 2009 Nov 8. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009. PMID: 19900832 Review.
Cited by
-
The Influence of BMP6 on Serotonin and Glucose Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7842. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147842. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063084 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary iron overload induces chronic pancreatitis and ferroptosis of acinar cells in mice.Int J Mol Med. 2023 Jan;51(1):9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5212. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36484371 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products as Modulators of Iron Metabolism and Ferroptosis in Diabetes and Its Complications.Nutrients. 2025 Aug 21;17(16):2714. doi: 10.3390/nu17162714. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40871742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP6) antagonises experimental proliferative vitreoretinopathy established by TGF-β2 stimulation in retinal pigment epithelial cells through modulation of the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways.Cell Tissue Res. 2024 Apr;396(1):103-117. doi: 10.1007/s00441-024-03870-1. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Cell Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 38403744
References
-
- Daher R, Kannengiesser C, Houamel D, Lefebvre T, Bardou-Jacquet E, Ducrot N, de Kerguenec C, Jouanolle AM, Robreau AM, Oudin C, et al. Heterozygous mutations in BmP6 pro-peptide lead to inappropriate hepcidin synthesis and moderate iron overload in humans. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:672–683,e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.10.049. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

